41 0 0 0 OA 腹部トレーニング7種目における腹直筋上部,腹直筋下部,外腹斜筋および大腿直筋の筋電図学的研究
- 著者
- 半田 徹 加藤 浩人 長谷川 伸 岡田 純一 加藤 清忠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.1, pp.43-54, 2009-06-30 (Released:2009-11-05)
- 参考文献数
- 27
The purpose of this study was to examine muscle activities during seven traditional different free dynamic exercises designed to strengthen the abdominal muscles. Eleven adult men with experience in weight training were asked to perform three repetitions of LSU, BSU, TSU, TC, RSU, LR and SLR. Activities of the upper rectus abdominis (URA), lower rectus abdominis (LRA), external abdominal oblique (EAO), and rectus femoris (RF) during the hip flexion and hip extension phases of each exercise were examined by electromyography (EMG) and analyzed using root mean square (RMS) values. The following results were obtained: (1) The mean RMS values for the URA were larger during the RSU and SLR than during the other five exercises. The value for the same muscle was larger during the TC exercise than during the LSU, BSU, TSU, and LR exercises. The mean RMS value for the LRA was largest during the RSU exercise, while that during the SLR exercise was larger than those during the LSU, BSU, TSU, TC, and LR exercises. (2) The mean RMS value for the EAO was largest during the SLR exercise, while that during the RSU exercise was second-largest and that during the TSU exercise was third-largest. The mean RMS values for the RF were larger during the RSU and SLR than during the other five exercises. The smallest value for this muscle was recorded during the TC exercise. (3) In most of the exercises, RMS in the hip flexion phase was larger than in the hip extension phase, and each muscle exhibited a knee flexion phase/knee extension phase ratio of between 0.5 and 0.8. However, the ratio for EAO and RF exceeded this range. (4) The muscle activity for the RF muscle in the RSU and SLR exercises was large, implying excessive stress for the lumbar vertebrae. Nevertheless, these exercises induced active muscle activity, and appeared desirable to perform with sufficient attention to safety.These results suggest that RSU and SLR exercises are the most effective movements for stimulating the URA, LRA and EAO. Moreover, TC is an effective movement for training the URA, and TSU is an effective movement for training.
13 0 0 0 OA 慶応4年野州世直し一揆の再検討
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸三
- 出版者
- 小樽商科大学
- 雑誌
- 商学討究 (ISSN:04748638)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.2/3, pp.83-109, 1982-12-28
6 0 0 0 OA 昭和初期国号及び元首の称号統一に関する一考察
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸
- 出版者
- 法政大学史学会
- 雑誌
- 法政史学 = 法政史学 (ISSN:03868893)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, pp.97-118, 1992-03-24
5 0 0 0 IR 天保10年京都豊年踊りの絵画資料
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸三
- 出版者
- 大阪樟蔭女子大学
- 雑誌
- 大阪樟蔭女子大学学芸学部論集 (ISSN:18807887)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.43, pp.51-70, 2006-03
京都豊年踊りとは、天保10年(1839)3、4月京都市中におこった熱狂的な踊り現象をさす。本稿では、この豊年踊りの絵画資料を概括し、その伝播過程や絵画の共通性や特異性を検討する。まず木版刷りの史料を検討した。京都で発行された一枚刷り「豊熟都大踊」「みやこおどり 鈴なるこの神徳」(大阪府立中之島図書館)や木版本『町々吉兆都繁栄』(早稲田大学附属図書館)は、この踊りの情報を各地へ伝える役割をはたした。たとえば後者は、『天保雑記』(国立公文書館内閣文庫)や『藤岡屋日記』(東京都公文書館)にそのまま書写されている。次に図巻・屏風の資料を検討した。図巻としては、「蝶々踊図巻」(大阪歴史博物館)と「天保十年豊年踊図巻」(チェスター・ビーティ・ライブラリー、アイルランド共和国ダブリン市)が双璧をなす。また「天保踊図屏風」(京都市歴史資料館)について、写真をかかげ、関連史料と合わせて紹介した。最後に冊子のさし絵を検討した。なかでも「天保視聴記事」(愛知県西尾市立図書館岩瀬文庫)のさし絵は図巻に匹敵し、『天保踊之記』(愛知県大洲市立図書館矢野玄道文庫)は、踊りに使われた衣装や提灯・手燭を図入りで説明している。これらの資料は、文字資料(文書・記録)とあわせて、豊年踊りの実状を詳細に明らかにするであろう。
4 0 0 0 OA 薬剤師の集中治療室専従化による薬物治療への影響
- 著者
- 中薗 健一 高野 尊行 根本 真人 長谷川 伸之
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本臨床救急医学会
- 雑誌
- 日本臨床救急医学会雑誌 (ISSN:13450581)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.6, pp.761-765, 2014-12-31 (Released:2015-01-24)
- 参考文献数
- 18
集中治療室(ICU)では,時間経過とともに刻々と変化する病態に合わせた薬物治療計画が必要である。そのため,薬剤師による迅速な薬学的介入は重要であると考えられる。今回,ICU専従薬剤師による全身管理への薬学的関与の影響について検討した。方法:那須赤十字病院ICUへ入室した患者を対象とした。2010年1月から12月の270名を専従前群,2013年1月の49名を専従後群とした。薬剤管理指導記録から薬学的介入の内容,薬物治療変更の有無について比較検討した。結果:薬剤管理指導実施率は専従前64.1%から,専従後91.8%へ有意に増加した。薬学的介入による薬物治療変更は,専従前51.3%,専従後73.2%へ有意な増加を認めた。考察:ICUへの薬剤師専従化により,薬学的介入件数,薬物治療変更率はともに増加した。これより,患者の病態変化に合わせた迅速な薬学的介入を行うことができた。
3 0 0 0 OA 投球動作における軸脚の股関節周囲筋の筋電図学的分析
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸
- 出版者
- 九州共立大学
- 雑誌
- 九州共立大学研究紀要 = Study journal of Kyushu Kyoritsu University (ISSN:21860483)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.5, no.1, pp.23-28, 2014-09-30
The purpose of this study was to investigate the muscle activation levels of the hip muscles duringpitching motion as ball speed was increased. Six college baseball pitchers were participated in thisstudy. Surface electromyography data were recorded in pivot leg from 6 muscles : adductor longus(AL), gracilis (GR), adductor magnus (AM), rectus femoris (RF) , biceps femoris (BF) and gluteus medius(GM). The pitching motion was divided into 5 distinct phases: wind-up, early cocking, late cocking,acceleration, follow-through. The results demonstrated that high level muscle activity (greater than 40%maximal voluntary contraction) was found in GM during early cocking phase, and in AL, GR, AM andBF during late cocking phase, and in AL, GR and BF during acceleration phase. Then, the activity levelof the hip muscles in the slow ball pitching and fast ball pitching was compared. Significantly highermuscle activity was showed in fast ball pitching in AL, GM, and BF during early cocking phase, in BFand AL during late cocking phase, and in AL, GM, and RF during acceleration phase. The findings fromthis study indicate that high muscle activity have been shown in the abductor of the hip joint duringearly cocking phase that produce translational movement, and high muscle activity have been shown inthe adductor and extensor of the hip joint during late cocking phase and acceleration phase that producerotational movement.
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, pp.154_2-154_2, 2017
<p> 本研究では投球速度の異なる野球投手の筋厚を比較し、高い投球速度を示す投手の形態的特徴を明らかにすることを目的とした。2016、2017年の春季オープン戦に登板した投手を対象に全投球の球速上位20%の平均値を算出し、140km/h以上を高速群(n=7)、130km/h未満を低速群(n=9)として抽出した。筋厚測定には超音波診断装置を使用した。撮像部位は両側の前腕部、上腕部(前・後部)、胸部、腹部、側腹部、肩甲棘部(上・下部)、肩甲骨内側部・肩甲下部、腰部、臀部(後・側部)、大腿部(前・後部)、下腿部(前・後部)であり、これらの17部位より29筋を測定の対象とした。部位別の比較において高速群では投球側の前腕部、腰部、臀部、大腿後部、下腿後部、非投球側の腹部、側腹部、大腿前部、臀部、大腿後部、下腿後部において低速群よりも高い筋厚を示した。また、筋別の比較において高速群は投球側の脊柱起立筋、大殿筋、大腿二頭筋、腓腹筋、非投球側の腹直筋、内腹斜筋、脊柱起立筋、大腿二頭筋において低速群よりも高い筋厚を示した。これら結果より投球速度の高速群では体幹、下肢筋群の発達が顕著であることが示唆された。</p>
2 0 0 0 IR 投球動作における軸脚の股関節周囲筋の筋電図学的分析
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸
- 出版者
- 九州共立大学
- 雑誌
- 九州共立大学研究紀要 = Study journal of Kyushu Kyoritsu University (ISSN:21860483)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.5, no.1, pp.23-28, 2014
The purpose of this study was to investigate the muscle activation levels of the hip muscles duringpitching motion as ball speed was increased. Six college baseball pitchers were participated in thisstudy. Surface electromyography data were recorded in pivot leg from 6 muscles : adductor longus(AL), gracilis (GR), adductor magnus (AM), rectus femoris (RF) , biceps femoris (BF) and gluteus medius(GM). The pitching motion was divided into 5 distinct phases: wind-up, early cocking, late cocking,acceleration, follow-through. The results demonstrated that high level muscle activity (greater than 40%maximal voluntary contraction) was found in GM during early cocking phase, and in AL, GR, AM andBF during late cocking phase, and in AL, GR and BF during acceleration phase. Then, the activity levelof the hip muscles in the slow ball pitching and fast ball pitching was compared. Significantly highermuscle activity was showed in fast ball pitching in AL, GM, and BF during early cocking phase, in BFand AL during late cocking phase, and in AL, GM, and RF during acceleration phase. The findings fromthis study indicate that high muscle activity have been shown in the abductor of the hip joint duringearly cocking phase that produce translational movement, and high muscle activity have been shown inthe adductor and extensor of the hip joint during late cocking phase and acceleration phase that producerotational movement.
2 0 0 0 OA 投球速度の高い野球投手における四肢、体幹筋の形態的特性
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸
- 出版者
- 九州共立大学
- 雑誌
- 九州共立大学研究紀要 = Study journal of Kyushu Kyoritsu University (ISSN:21860483)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.9, no.1, pp.49-56, 2018-09-28
The purpose of this study was to investigate the characteristics of the muscle morphology of limbsand trunk in baseball pitchers with high ball speed. The high ball speed group (average ball speed isover 140 km/h : n=7) and the low ball speed group (average ball speed less than 130 km/h : n=9) werecompared for muscle mass and muscle thickness. Muscle thickness was measured bilaterally with B-modeultrasonography. In the lean body mass and muscle mass (whole body, upper limbs, lower limbs andtrunk), the high ball speed group showed a significantly higher value than the low ball speed group. Incomparing the muscle thickness of muscle groups, the high ball speed group showed significantly greatermuscle thickness at 5 sites (forearm, lumbar superficial, buttocks, back of thigh, posterior lower leg) onthe throwing side than the low ball speed group. On the other hand, the high ball speed group showedsignificantly greater muscle thickness at 6 sites (anterior abdomen, lateral abdomen, lumbar superficial,buttocks, back of thigh, posterior lower leg) on the nonthrowing side than the low ball speed group.In the comparison of the muscle thickness of individual muscles, the high ball speed group showedsignificantly greater muscle thickness in 3 muscles (spinal erector, gluteus maximus, gastrocnemius) onthe throwing side than the low ball speed group. Also, the high ball speed group showed significantlygreater muscle thickness in 7 muscles (pectoralis minor, rectus abdominis, abdominal internal oblique,transversus abdominal, erector spinae, gluteus maximus, biceps femoris) on the non-throwing sidethan the low ball speed group. These results indicate that baseball pitchers with high ball speed have agreater muscle thickness in trunk rotators and leg extensors.
- 著者
- 半田 徹 加藤 浩人 長谷川 伸 岡田 純一 加藤 清忠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.0907160099, (Released:2009-07-20)
- 参考文献数
- 27
The purpose of this study was to examine muscle activities during seven traditional different free dynamic exercises designed to strengthen the abdominal muscles. Eleven adult men with experience in weight training were asked to perform three repetitions of LSU, BSU, TSU, TC, RSU, LR and SLR. Activities of the upper rectus abdominis (URA), lower rectus abdominis (LRA), external abdominal oblique (EAO), and rectus femoris (RF) during the hip flexion and hip extension phases of each exercise were examined by electromyography (EMG) and analyzed using root mean square (RMS) values. The following results were obtained: (1) The mean RMS values for the URA were larger during the RSU and SLR than during the other five exercises. The value for the same muscle was larger during the TC exercise than during the LSU, BSU, TSU, and LR exercises. The mean RMS value for the LRA was largest during the RSU exercise, while that during the SLR exercise was larger than those during the LSU, BSU, TSU, TC, and LR exercises. (2) The mean RMS value for the EAO was largest during the SLR exercise, while that during the RSU exercise was second-largest and that during the TSU exercise was third-largest. The mean RMS values for the RF were larger during the RSU and SLR than during the other five exercises. The smallest value for this muscle was recorded during the TC exercise. (3) In most of the exercises, RMS in the hip flexion phase was larger than in the hip extension phase, and each muscle exhibited a knee flexion phase/knee extension phase ratio of between 0.5 and 0.8. However, the ratio for EAO and RF exceeded this range. (4) The muscle activity for the RF muscle in the RSU and SLR exercises was large, implying excessive stress for the lumbar vertebrae. Nevertheless, these exercises induced active muscle activity, and appeared desirable to perform with sufficient attention to safety.These results suggest that RSU and SLR exercises are the most effective movements for stimulating the URA, LRA and EAO. Moreover, TC is an effective movement for training the URA, and TSU is an effective movement for training.
2 0 0 0 OA 入院患者にとってのカーテンの役割を考える
2 0 0 0 OA 筋力トレーニングのプル系5種目における上腕二頭筋, 広背筋および僧帽筋の筋電図学的研究
- 著者
- 半田 徹 加藤 浩人 長谷川 伸 岡田 純一 加藤 清忠
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人日本体力医学会
- 雑誌
- 体力科学 (ISSN:0039906X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.2, pp.159-168, 2005 (Released:2006-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 3 7
To compare the effectiveness of five different muscle training movements on the biceps brachii, latissimus dorsi and trapezius muscles, eight weight-trained men (age, 20.4±0.5 years) were asked to perform three repetitions, at 70% one repetition maximum, of upright rowing (UR) and bent-over rowing (BR) exercises using a barbell ; and seated rowing (SR), front lat pull-down (LPf) and back lat pull-down (LPb) exercises using a Universal Machine. The activities of the biceps brachii, latissimus dorsi, and trapezius during the elbow flexsion and elbow extension phases of each exercise were analyzed using integrated electromyography (EMG) and normalized I-EMG. The results were as follows :1. The mean nrmsEMG values for the biceps brachii were larger during UR and LPf exercises than during BR, SR, and LPb exercises, suggesting that UR and LPf are more effective than the other movements for training the biceps brachii. The mean nrmsEMG values for the latissimus dorsi were larger during SR, LPf, and LPb exercises, followed by BR and UR exercises (in descending order), suggesting that SR, LPf, and LPb exercises are more effective than the other movements for training the latissimus dorsi.2. The mean nrmsEMG values for the upper trapezius were larger during UR and BR exercises than during SR, LPf, and LPb exercises, suggesting that UR and BR exercises are more effective than the other movements for training the upper trapezius. The mean nrmsEMG values for the middle trapezius were larger during BR and SR exercises than during UR, LPf, and LPb exercises, suggesting that BR and SR exercises are more effective than the other movements for training the middle trapezius. The mean nrmsEMG values for the lower trapezius were larger during BR exercise than during other movements, suggesting that BR exercise is more effective than the other movements for training the lower trapezius.3. In all the exercises, each muscle showed a higher nrmsEMG value during the elbow flexsion phase than during the elbow extension phase. This observation suggests that the training method examined in this study should emphasize the elbow flexsion movement.The present results suggest that UR exercise is the most effective movement for training the biceps brachii and upper trapezius, BR is most effective for training the upper trapezius, middle trapezius and lower trapezius, SR is most effective for training the latissimus dorsi and middle trapezius, LPf is most effective for training the biceps brachii and latissimus dorsi, and LPb is most effective for training the latissimus dorsi.
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸
- 出版者
- 法政大学史学会
- 雑誌
- 法政史学 (ISSN:03868893)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.58, pp.85-88, 2002-09
2 0 0 0 感染症発生動向調査 : 流行警報・注意報発令モデルの検討
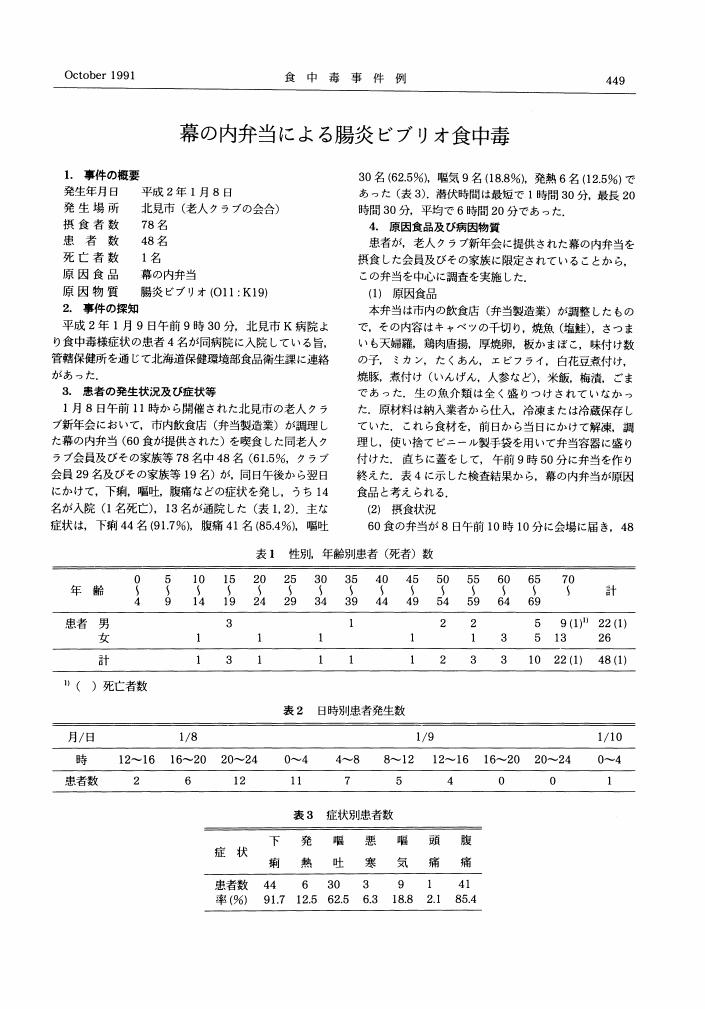
1 0 0 0 OA 幕の内弁当による腸炎ビブリオ食中毒
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸作
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本食品衛生学会
- 雑誌
- 食品衛生学雑誌 (ISSN:00156426)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.5, pp.449-450, 1991-10-05 (Released:2009-12-11)
1 0 0 0 OA 野球投手のスプリント能力と投球速度の関係
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸 久保 誠司
- 雑誌
- 九州共立大学研究紀要 = Study journal of Kyushu Kyoritsu University (ISSN:21860483)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.2, pp.85-90, 2023-02-28
The purpose of this study was to clarify the relationship between sprinting ability and ball speed incollege baseball pitchers, and to examine the evaluation method of sprinting ability considering bodyweight and lean body mass. Thirty-one college baseball pitchers participated in this study. Height,weight, lean body mass, body fat mass, muscle mass, and skeletal muscle mass were measured, andbody fat percentage, body mass index (BMI), and skeletal muscle index (SMI) were calculated. Ball speedwas measured using Rapsodo pitching 2.0. The baseball pitcher was asked to throw 10 full pitches fromthe pitcher's mound toward the catcher. Maximum ball speed was used as an index of ball speed. Toevaluate sprint ability, sprint times of 10m, 30m, 50m, 100m, 200m, and 400m were measured, andrunning speed, momentum, and kinetic energy were calculated. Pearson's product-moment correlationcoefficient was calculated to investigate the relationship between the measured indices. Ball speed wassignificantly correlated with body weight, BMI, lean body mass, muscle mass, and SMI. In addition,ball speed showed a significant negative correlation with running speed in 200m and 400m sprints, and showed a significant positive correlation with momentum and kinetic energy in 10m, 30m, 50m,and 100m sprints. The results of this study suggest the importance of considering body weight whenevaluating the sprinting ability of baseball pitchers.
1 0 0 0 OA 投球速度と筋力および筋量の関係
1 0 0 0 OA 05バ-12-ポ-33 野球投手の肩関節可動域と投球速度の関係
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集 第70回(2019) (ISSN:24241946)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.185_1, 2019 (Released:2019-12-20)
本研究では大学野球投手24名を対象として、投球側と非投球側の他動的肩関節可動域(外旋可動域、内旋可動域、総回旋可動域)とその両側差、および投球速度(最高速度、平均速度)の測定を行い、投球側と非投球側の肩関節可動域の特性、および肩関節可動域と投球速度の関係を明らかにすることを目的とした。その結果、投球側と非投球側の比較において、肩関節の外旋可動域では投球側が非投球側に対して有意に高い値を示し(p<0.001)、内旋可動域では非投球側が投球側に対して有意に高い値を示した(p<0.001)。また、肩関節可動域と投球速度の関係では、投球側の肩関節外旋可動域(p<0.05)と外旋可動域の両側差(p<0.05)、総回旋可動域(p<0.01)と総回旋可動域の両側差(p<0.05)の4つの指標と最高球速および平均球速との間に有意な正の相関関係が認められた。このことから、肩関節の外旋可動域、およびそれに伴う総回旋可動域の大きさは投球速度を決定する要因の1つとなりうることが示唆された。
1 0 0 0 OA 感染症流行周期に影響を及ぼす環境要因 —感染症発生動向調査(1981—2002年)—
- 著者
- 長谷川 伸作 井上 仁 陶山 昭彦 徳永 章二
- 出版者
- 独立行政法人 科学技術振興機構 情報事業本部
- 雑誌
- 情報科学技術研究集会予稿集 第40回情報科学技術研究集会予稿集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.A62, 2003 (Released:2003-11-14)
- 参考文献数
- 14
感染症の流行周期、流行パターンには様々な環境要因が影響を及ぼすと考えられる。感染症発生動向調査1981年からの22年間データの時系列解析により、都道府県別感染症の流行周期特性を明らかにした。また流行の周期特性に影響を及ぼすと考えられる要因について検討した。流行周期解析の結果、感染症それぞれの固有の、また地域特有の流行周期、流行パターンが示された。水痘は通年発生で、季節的流行を示した。風疹は1年の他に5年周期の大流行を示し、流行性耳下腺炎は通年発生で4年周期、麻疹は1,3,7年周期、数年毎の大流行と季節変動を反映した1年周期の極小波を示した。流行周期に影響を及ぼす要因の検討から、水痘、風疹、手足口病などの流行周期特性は温量指数·寒さの指数に大きく影響を受け、麻疹、流行性耳下腺炎では人の接触度合いとの関連が顕著であることが示された。