- 著者
- Yanchang WANG Sangmin LEE Kentaro YAMAMOTO Toshiyuki MATSUNAGA Hidenori MIKI Hideki IBA Koichi TSUCHIYA Tomoki UCHIYAMA Toshiki WATANABE Tsuyoshi TAKAMI Yoshiharu UCHIMOTO
- 出版者
- The Electrochemical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Electrochemistry (ISSN:13443542)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22-00133, (Released:2023-01-28)
3 0 0 0 OA リフティングボディ飛行実験(LIFLEX)システム開発
- 著者
- 中安 英彦 塚本 太郎 南 吉紀 石本 真二 藤井 謙司 栗田 充 青木 良尚 麥谷 高志 鷲谷 正史 山本 行光 石川 和敬 冨田 博史 元田 敏和 二宮 哲次郎 濱田 吉郎 舩引 浩平 津田 宏果 牧 緑 小野 孝次 廣谷 智成 LIFLEXチーム Nakayasu Hidehiko Tsukamoto Taro Minami Yoshinori Ishimoto Shinji Fujii Kenji Kurita Mitsuru Aoki Yoshihisa Mugitani Takashi Washitani Masahito Yamamoto Yukimitsu Ishikawa Kazutoshi Tomita Hiroshi Motoda Toshikazu Ninomiya Tetsujiro Hamada Yoshiro Funabiki Kohei Tsuda Hiroka Maki Midori Ono Takatsugu Hirotani Tomonari LIFLEX Team
- 出版者
- 宇宙航空研究開発機構
- 雑誌
- 宇宙航空研究開発機構研究開発報告 = JAXA Research and Development Report (ISSN:13491113)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.JAXA-RR-10-004, 2010-09-30
宇宙航空研究開発機構では,次世代の再使用宇宙輸送システムの様々なコンセプトについて検討してきたが,その中の有望なものの一つとしてリフティングボディ形状の往還システムがある.これは翼をもたず,胴体の形状によって揚力を発生するタイプの機体であり,構造の軽量化,高い容積効率,極超音速域での空力加熱特性の観点から優位性があるとされている.一方,リフティングボディ形状は揚抗比が小さく,また低速時の安定性/ 制御性が弱いため,ALFLEX(小型自動着陸実験1996)のような翼胴型の機体に比較して滑走路への進入/ 着陸時に困難がある.そこで,リフティングボディ形状の往還システムを実現するうえで最も重要な技術課題の一つとなっている自動着陸技術の蓄積を主目的とした飛行実験を,小規模で低コストな機体を用いて行うことを計画した.本報告では,飛行実験計画および実験システムの概要と,地上試験やヘリコプタを用いた懸吊飛行試験を含む開発のプロセスについて詳述する.
- 著者
- Kota Yamamoto Yuko Takizawa Yoshito Chikaraishi
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Organic Geochemists
- 雑誌
- Researches in Organic Geochemistry (ISSN:13449915)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.1, pp.7-12, 2022-12-27 (Released:2023-03-15)
- 参考文献数
- 20
Difference in the stable nitrogen isotope ratio (δ15N value) between two types of amino acids within a single organism has been employed as a powerful tool for estimating the trophic position (TP) of the organism in food webs. However, accuracy of the TP values estimated relies on the consistency of trophic elevation in the δ15N value across diverse organisms and among diverse environments. Indeed, little is known the applicability of this tool for organisms found in cold environments. In the present study, we determined the δ15N values of amino acids for 10 species collected in a coastal marine environment of Hokkaido, a humid continental climate zone in Japan, to evaluate whether this tool is applicable to marine species found in cold regions. The δ15N values of glutamic acid and phenylalanine determined in the present study illustrate diverse TP values for the species, as 0.7-1.0 for primary producers (i.e., macroalgae), 1.9-2.3 for herbivores (e.g., zooplankton and sea urchin), and 2.3-3.7 for omnivores and carnivores (e.g., crab and fish). These results indicate that the TP values estimated in the present study are basically consistent with actual TP for producers and herbivores and with the literature TP values for the same or similar species of omnivores and carnivores from temperate regions, and thus provide evidence that this tool is basically applicable to estimate the TP of marine species found in cold regions. On the other hand, low TP value was estimated for one species, goby, suggesting that further studies will be required, particularly for identifying mechanisms responsible for the low TP values estimated for such species.
- 著者
- Ryo Sugawara Nana Shirasuka Tatsuki Yamamoto Kosuke Nagamune Kaito Oguchi Nitaro Maekawa Kozue Sotome Akira Nakagiri Shuji Ushijima Naoki Endo
- 出版者
- The Mycological Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mycoscience (ISSN:13403540)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.3, pp.102-117, 2022-05-31 (Released:2022-05-31)
- 参考文献数
- 66
- 被引用文献数
- 3
We describe two new species of resupinate Sistotrema sensu lato (Cantharellales) collected in Japan: S. flavorhizomorphae and S. chloroporum. Both species have urniform basidia with more than four sterigmata and monomitic hyphal system, oil-rich hyphae in subiculum, which is typical for this genus. Sistotrema chloroporum is characterized by poroid hymenophore partly yellowish-green, basidia 4-6-spored, medium-sized basidiospores (4.5-6.5 × 3.5-6 µm), and broadleaf forest habitat. Sistotrema flavorhizomorphae is characterized by hydnoid-irpicoid hymenophore, bright yellowish rhizomorphs, basidia 6-8-spored, small basidiospores (3-3.5 × 2.5-3 µm), and pine forest habitat. Phylogenetic trees inferred from the fungal nrDNA ITS and LSU and the rpb2 sequences supported that both species were distinct and grouped with other ectomycorrhizal Sistotrema and Hydnum species, but their generic boundary was unclear. Mycorrhizae underneath basidiomes of both species were identified and described via molecular techniques. Mycorrhizae of S. chloroporum have similar characteristics to those of other Sistotrema s.l. and Hydnum species, i.e., S. confluens and H. repandum, whereas S. flavorhizomorphae has a distinct morpho-anatomy, for example, a distinct pseudoparenchymatous mantle. Comprehensive characterizations of basidiomes and mycorrhizae improve the taxonomic analysis of mycorrhizal species of Sistotrema s.l.
- 著者
- Nobuyuki Kagiyama Misako Toki Akihiro Hayashida Minako Ohara Atsushi Hirohata Keizo Yamamoto Toshinori Totsugawa Taichi Sakaguchi Kiyoshi Yoshida Mitsuaki Isobe
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.11, pp.1730-1735, 2017-10-25 (Released:2017-10-25)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 6 8
Background:As mitral valve (MV) repair for Barlow’s disease remains surgically challenging, it is important to distinguish Barlow’s disease from fibroelastic deficiency (FED) preoperatively. We hypothesized that the prolapse volume to prolapse height ratio (PV-PH ratio) may be useful to differentiate Barlow’s disease and FED.Methods and Results:In 76 patients with MV prolapse who underwent presurgical transesophageal echocardiography, the 3D MV morphology was quantified: 19 patients were diagnosed with Barlow’s disease and 57 with FED. The patients with Barlow’s disease had greater prolapse volume and height than the patients with FED, as well as greater PV-PH ratio (0.61±0.35 vs. 0.17±0.10, P<0.001). Receiver-operating characteristic analysis revealed that with a cutoff value of 0.27, the PV-PH ratio differentiated Barlow’s disease from FED with 84.2% sensitivity and 84.2% specificity. Net reclassification improvement showed that the differentiating ability of the PV-PH ratio was significantly superior to prolapse volume (1.30, P<0.001). After being adjusted by each of prolapse volume and height, annular area and shape, and the number of prolapsed segments, the PV-PH ratio had an independent association with Barlow’s disease.Conclusions:The PV-PH ratio was able to differentiate Barlow’s disease from FED with high accuracy. 3D quantification including this value should be performed before MV repair.
- 著者
- ISHIOKA Keiichi YAMAMOTO Naoto FUJITA Masato
- 出版者
- Meteorological Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- 気象集誌. 第2輯 (ISSN:00261165)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-022, (Released:2021-12-28)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
In the discretization of the primitive equations for numerical calculations, a formulation of a three-dimensional spectral model is proposed that uses the spectral method not only in the horizontal direction but also in the vertical direction. In this formulation, the Legendre polynomial expansion is used for the vertical discretization. It is shown that semi-implicit time integration can be efficiently done under this formulation. Then, a numerical model based on this formulation is developed and several benchmark numerical calculations proposed in previous studies are performed to show that this implementation of the primitive equations can give accurate numerical solutions with a relatively small degrees of freedom in the vertical discretization. It is also shown that, by performing several calculations with different vertical degrees of freedom, a characteristic property of the spectral method is observed in which the error of the numerical solution decreases rapidly when the number of vertical degrees of freedom is increased. It is also noted that an alternative to the sponge layer can be devised to suppress the reflected waves under this formulation, and that a “toy” model can be derived as an application of this formulation, in which the vertical degrees of freedom are reduced to the minimum.
3 0 0 0 OA A New Nonpeptide Tachykinin NK1 Receptor Antagonist Isolated from the Plants of Compositae
- 著者
- Atsushi Yamamoto Ko Nakamura Kazuhito Furukawa Yukari Konishi Takashi Ogino Kunihiko Higashiura Hisashi Yago Kaoru Okamoto Masanori Otsuka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.1, pp.47-52, 2002 (Released:2002-03-19)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 21 32
To find new tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonists from natural sources, we examined the tachykinin antagonist activity in the extracts of approximately 200 species of plants by the use of isolated guinea pig ileum. As a result, we discovered a novel and potent NK1 receptor antagonist in the extract of dried flowers of Matricaria chamomilla L. (chamomile). The structure of the antagonist was established as N1, N5, N10, N14-tetrakis[3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoyl]-1, 5, 10, 14-tetraazatetradecane (tetracoumaroyl spermine, 1a). The Ki values of 1a, estimated from the inhibitory action on the substance P (SP)-induced contraction of the guinea pig ileum and the inhibition of the binding of [3H][Sar9, Met(O2)11]SP to human NK1 receptors, were 21.9 nM and 3.3 nM, respectively. 1a is the first potent NK1 receptor antagonist from natural sources and it has a unique structure of a polyacylated spermine. 1a was concentrated in pollen of Matricaria chamomilla L. and was also found in the extracts of flowers of other four species of Compositae. In addition, we found N1, N5, N10-tris[3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoyl]-1, 5, 10, 14-tetraazatetradecane (2) as a new compound in the extract of flowers of Matricaria chamomilla L., which did not exhibit any tachykinin antagonist activity. A number of related compounds were synthesized, and the structure–activity relationship was studied.
- 著者
- Yohei Tsuchikawa Yoshiyuki Tokuda Hideki Ito Miho Shimizu Shinya Tanaka Kazuki Nishida Daichi Takagi Akimasa Fukuta Natsuki Takeda Hiromasa Yamamoto Masaya Hori Yoshihiro Nishida Masato Mutsuga
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0416, (Released:2022-11-10)
- 参考文献数
- 20
Background: The effect of delayed ambulation on the outcome of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) remains to be clarified.Methods and Results: The long-term and in-hospital outcomes of 887 patients who underwent isolated CABG (455 off-pump cases, 135 urgent cases) were evaluated, with a focus on the timing of first ambulation. In-hospital mortality cases were excluded. Early ambulation (first ambulation within 3 days after operation) was achieved in 339 (38%) patients. In the multivariable logistic regression analysis, longer operation time and urgent case, EuroSCORE II, re-thoracotomy, and respiratory time were associated with delayed (≥4 days) ambulation. Delayed ambulation was associated with a high incidence of postoperative complications, such as pneumonia, and stroke (P<0.01). Following discharge, 22.2% of patients experienced major cardiac events and 13.8% died during the follow-up period (median follow-up 60 months). Cox hazards analysis revealed that delayed ambulation was associated with long-term adverse events (hazard ratio 1.04 per day, P<0.001). With adjustment for preoperative factors, the estimated future risk of adverse events was found to be increased day-by-day during the delay until initial ambulation.Conclusions: In isolated CABG patients, delayed ambulation was associated with poor outcomes, even in the long-term period. The results support the current guideline recommending early ambulation protocol after cardiac surgery.
3 0 0 0 IR イタリア語の中動態について(その2)
- 著者
- 山本 真司 ヤマモト シンジ YAMAMOTO Shinji
- 出版者
- 東京外国語大学
- 雑誌
- 東京外国語大学論集 (ISSN:04934342)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.80, pp.273-291, 2010
3 0 0 0 OA 植物のドメスティケーション : ジャガイモの栽培化 : ラクダ科動物との関係から考える
- 著者
- 大山 修一 山本 紀夫 近藤 史 Shuichi Oyama Norio Yamamoto Fumi Kondo
- 出版者
- 国立民族学博物館
- 雑誌
- 国立民族学博物館調査報告 = Senri Ethnological Reports (ISSN:13406787)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, pp.177-203, 2009-03-31
- 著者
- Keisuke Sato Yoshitsugu Yamamoto
- 出版者
- The Operations Research Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- 日本オペレーションズ・リサーチ学会論文誌 (ISSN:04534514)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.2, pp.112-130, 2009 (Released:2017-06-27)
- 参考文献数
- 12
This paper presents a study on the recently proposed linear inequality representation of Arrovian Social Welfare Functions (ASWFs). We correct and show several sufficient conditions on preference domains for the linear inequalities of the representation to form integral polytopes. We also show that a given probabilistic ASWF induces a real vector satisfying the inequalities.
3 0 0 0 OA Protective Effects of the Alga Fucoidan Against Amyloid-β-Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
- 著者
- Miki Nagata Mayumi Tsuji Tatsunori Oguchi Yutaro Momma Tetsuhito Nohara Hideaki Ohashi Naohito Ito Ken Yamamoto Yuko Udaka Akiko Sasaki Yuji Kiuchi Satoshi Numazawa
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- BPB Reports (ISSN:2434432X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.6, pp.206-213, 2021 (Released:2021-12-27)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Dementia is expected to affect an increasing number of patients with global aging populations. About 70% of all dementia is related to Alzheimer's disease (AD). Overaccumulation of amyloid-β protein (Aβ) in the brain forms senile plaques, one of the main features of neurodegeneration in AD. However, there are few drugs available to specifically inhibit senile plaque formation. Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide derived from brown algae, has various bioactivities, such as anti-tumoral and anti-obesity effects. This study aimed to clarify the mechanism underlying the protective effect of fucoidan against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Cell viability and Aβ-induced cytotoxicity were measured by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, calcein AM, and ethidium homodimer-1. Aβ-induced oxidative stress was evaluated through reactive oxygen species (ROS), cell membrane phospholipid peroxidation, mitochondrial ROS, and Mn-SOD, a mitochondrial radical scavenger. In addition, mitochondrial membrane permeability transition, and ATP concentration were evaluated. Fucoidan significantly improved Aβ-reduced cell viability. With respect to oxidative stress, Aβ exposure increased ROS, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial ROS, while fucoidan significantly suppressed these changes. Fucoidan also suppressed the decline in mitochondrial permeability transition and ATP caused by Aβ. Therefore, through its numerous antioxidant activities, fucoidan might have a neuroprotective role in preventing Aβ-induced neurotoxicity.
- 著者
- Masato Nishi Seiji Takashio Mami Morioka Akira Fujiyama Naoya Nakashima Kyoko Hirakawa Shinsuke Hanatani Hiroki Usuku Eiichiro Yamamoto Masafumi Kidoh Seitaro Oda Ryosuke Gushima Kenichi Matsushita Satoshi Fukushima Mitsuharu Ueda Kenichi Tsujita
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-22-0118, (Released:2022-05-21)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Background: The accurate sensitivity of amyloid deposition in extracardiac tissue (subcutaneous tissue and gastrointestinal tract) has not been evaluated in transthyretin amyloidosis cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) patients. This study aimed to evaluate the sensitivity of amyloid deposition in obtained endomyocardial and extracardiac biopsies.Methods and Results: This study retrospectively evaluated 175 consecutive ATTR-CM patients (wild-type [ATTRwt]: 134, hereditary [ATTRv]: 41) who had positive findings on 99 mTc-labeled pyrophosphate (99 mTc-PYP) scintigraphy and underwent tissue biopsy of at least one organ (subcutaneous tissue, gastrointestinal tract, and endomyocardium). Amyloid deposition was observed in the subcutaneous tissue of 57/150 patients (38%), gastrointestinal tract of 80/131 patients (61%), and endomyocardium of 108/109 patients (99%). Compared to patients with ATTRv, ATTRwt had significantly lower sensitivity in subcutaneous tissue (73% vs. 25%, P<0.01) and tended to be lower in the gastrointestinal tract (74% vs. 57%, P=0.08) biopsies. Among 124 patients who underwent both subcutaneous tissue and gastrointestinal tract biopsies, amyloid was detected in at least 1 specimen in 91 (73%) patients. The sensitivity of the combination of extracardiac biopsies was 66% and 94% in ATTRwt-CM and ATTRv-CM, respectively. Multivariate analysis reveals that ATTRv was the only significant predictor of amyloid deposition in the subcutaneous tissue.Conclusions: Subcutaneous tissue and gastrointestinal tract biopsy sensitivity are inadequate, especially in patients with ATTRwt; however, the combination of these extracardiac biopsies contributes to increased sensitivity in patients with positive 99 mTc-PYP scintigraphy findings.
- 著者
- Yasuaki Takeji Tomohiko Taniguchi Takeshi Morimoto Shinichi Shirai Takeshi Kitai Hiroyuki Tabata Kazuki Kitano Nobuhisa Ono Ryosuke Murai Kohei Osakada Koichiro Murata Masanao Nakai Hiroshi Tsuneyoshi Tomohisa Tada Masashi Amano Hiroki Shiomi Hirotoshi Watanabe Yusuke Yoshikawa Ko Yamamoto Mamoru Toyofuku Shojiro Tatsushima Norino Kanamori Makoto Miyake Hiroyuki Nakayama Kazuya Nagao Masayasu Izuhara Kenji Nakatsuma Moriaki Inoko Takanari Fujita Masahiro Kimura Mitsuru Ishii Shunsuke Usami Kenichiro Sawada Fumiko Nakazeki Marie Okabayashi Manabu Shirotani Yasutaka Inuzuka Tatsuhiko Komiya Kenji Minatoya Takeshi Kimura on behalf of the CURRENT AS Registry-2 Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-1062, (Released:2022-04-19)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: There is scarce data evaluating the current practice pattern and clinical outcomes for patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS), including both those who underwent surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) or transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) and those who were managed conservatively in the TAVI era.Methods and Results: The Contemporary outcomes after sURgery and medical tREatmeNT in patients with severe Aortic Stenosis (CURRENT AS) Registry-2 is a prospective, physician-initiated, multicenter registry enrolling consecutive patients who were diagnosed with severe AS between April 2018 and December 2020 among 21 centers in Japan. The rationale for the prospective enrollment was to standardize the assessment of symptomatic status, echocardiographic evaluation, and other recommended diagnostic examinations such as computed tomography and measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide. Moreover, the schedule of clinical and echocardiographic follow up was prospectively defined and strongly recommended for patients who were managed conservatively. The entire study population consisted of 3,394 patients (mean age: 81.6 years and women: 60%). Etiology of AS was degenerative in 90% of patients. AS-related symptoms were present in 60% of patients; these were most often heart failure symptoms. The prevalence of high- and low-gradient AS was 58% and 42%, respectively, with classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient AS in 4.5% and 6.7%, respectively.Conclusions: The CURRENT AS Registry-2 might be large and meticulous enough to determine the appropriate timing of intervention for patients with severe AS in contemporary clinical practice.
- 著者
- Yuya Matsuda Shunsaku Nakagawa Ikuko Yano Satohiro Masuda Satoshi Imai Atsushi Yonezawa Takashi Yamamoto Mitsuhiro Sugimoto Masahiro Tsuda Tetsunori Tsuzuki Tomohiro Omura Takayuki Nakagawa Toyofumi Fengshi Chen-Yoshikawa Miki Nagao Hiroshi Date Kazuo Matsubara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.4, pp.397-402, 2022-04-01 (Released:2022-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Invasive Aspergillus infection is a major factor for poor prognosis in patients receiving lung transplantation (LT). An antifungal agent, itraconazole (ITCZ), that has antimicrobial activity against Aspergillus species, is used as a prophylactic agent against Aspergillus infection after LT. ITCZ and its metabolite, hydroxyitraconazole (OH-ITCZ), potently inhibit CYP3A and P-glycoprotein that metabolize or excrete calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs), which are the first-line immunosuppressants used after LT; thus, concomitant use of ITCZ and CNIs could induce an increase in the blood concentration of CNIs. However, no criteria for dose reduction of CNIs upon concomitant use with ITCZ in LT recipients have been defined. In this study, the effect of ITCZ and OH-ITCZ on the blood concentrations of two CNIs, tacrolimus and cyclosporine, after LT were retrospectively evaluated. A total of 39 patients who received LT were evaluated. Effects of ITCZ and OH-ITCZ on the concentration/dosage (C/D) ratio of tacrolimus and cyclosporine were analyzed using linear mixed-effects models. The plasma concentrations of OH-ITCZ were about 2.5-fold higher than those of ITCZ. Moreover, there was a significant correlation between the plasma concentrations of ITCZ and OH-ITCZ. Based on parameters obtained in the linear regression analysis, the C/D ratios of cyclosporine and tacrolimus increase by an average of 2.25- and 2.70-fold, respectively, when the total plasma concentration of ITCZ plus OH-ITCZ is 1000 ng/mL. In conclusion, the plasma levels of ITCZ and OH-ITCZ could be key factors in drawing up the criterion for dose reduction of CNIs.
- 著者
- Mariko Kimoto Toshiyasu Sakane Hidemasa Katsumi Akira Yamamoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.2, pp.138-145, 2022-02-01 (Released:2022-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
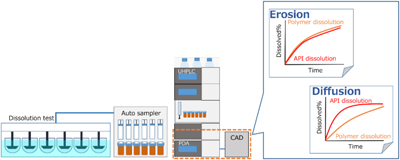
The dissolution behaviors of base excipients from sustained-release formulations have been investigated using various methodologies. However, the dissolution of polymers has not been fully evaluated because differences between formulations are still verified only by the release of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). In our previous study, we proposed a quick and simultaneous analysis of dissolved APIs and water-soluble polymers by ultra HPLC using charged aerosol and photodiode array detectors. The purpose of this study was to verify whether the analysis system could be adapted to other water-soluble polymers. Dissolution tests were conducted using matrix model tablets prepared from three polymers and three APIs (propranolol, ranitidine, and cilostazol) with different solubilities. The dissolution profiles of the polymers and APIs were determined using the proposed analysis system and compared. The results clarified differences in the dissolution behaviors of the APIs and polymers. The polymers, especially hydroxypropyl cellulose, exhibited the dissolution properties characteristic of each model formulation. Propranolol and ranitidine showed the diffusion type, while cilostazol showed the erosion type release mechanism due to their different solubilities. The release of cilostazol was delayed in all models compared to the polymer, which may be due to the aggregation of cilostazol in the gel layer. This analytical method can be used to study the dissolution behavior (diffusion or erosion) of APIs from matrix tablets containing various polymers. This method will provide useful information on release control, which will make it easier and more efficient to design appropriate formulations and analyze the release mechanisms.
- 著者
- Koichi Tomoda Kaoru Kubo Kazuo Hino Yasunori Kondoh Yasue Nishii Noriko Koyama Yoshifumi Yamamoto Masanori Yoshikawa Hiroshi Kimura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Toxicology
- 雑誌
- The Journal of Toxicological Sciences (ISSN:03881350)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.331-337, 2014-04-01 (Released:2014-03-18)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 5 7
Cigarette smoke induces skeletal muscle wasting by a mechanism not yet fully elucidated. Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) in the skeletal muscles are useful energy sources during exercise or systemic stresses. We investigated the relationship between skeletal muscle wasting caused by cigarette smoke and changes in BCAA levels in the plasma and skeletal muscles of rats. Furthermore, the effects of BCAA-rich diet on muscle wasting caused by cigarette smoke were also investigated. Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats that were fed with a control or a BCAA-rich diet were exposed to cigarette smoke for four weeks. After the exposure, the skeletal muscle weight and BCAA levels in plasma and the skeletal muscles were measured. Cigarette smoke significantly decreased the skeletal muscle weight and BCAA levels in both plasma and skeletal muscles, while a BCAA-rich diet increased the skeletal muscle weight and BCAA levels in both plasma and skeletal muscles that had decreased by cigarette smoke exposure. In conclusion, skeletal muscle wasting caused by cigarette smoke was related to the decrease of BCAA levels in the skeletal muscles, while a BCAA-rich diet may improve cases of cigarette smoke-induced skeletal muscle wasting.
- 著者
- Natsuko SUGIURA Kazuhiko OCHIAI Toshiaki YAMAMOTO Takuya KATO Yoshi KAWAMOTO Toshinori OMI Shin-ichi HAYAMA
- 出版者
- JAPANESE SOCIETY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE
- 雑誌
- Journal of Veterinary Medical Science (ISSN:09167250)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.4, pp.479-482, 2020 (Released:2020-04-09)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 1
We analyzed the genotypes of three pregnant females and their litters to investigate the phenomenon of multiple paternity in wild raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) using 17 microsatellite markers. If a female has mated with only one male during estrus, then the maximum number of paternal alleles will not exceed two among littermates with the same father. The results revealed two out of three litters had three or four paternal alleles at one or five microsatellite loci. Therefore, the female had mated with more than one male during estrus. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to report the possibility of multiple paternity in wild raccoon dogs.
3 0 0 0 OA 看護師を目指す留学生のためのライティング教材の開発とその活用
- 著者
- 山元 一晃 浅川 翔子 加藤 林太郎 Kazuaki YAMAMOTO Shoko ASAKAWA Rintaro KATO
- 出版者
- 金城学院大学
- 雑誌
- 金城学院大学論集. 人文科学編 = Treatises and Studies by the Facalty of Kinjo Gakuin University. Studies in Humanities (ISSN:18800351)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.1, pp.129-139, 2021-09-30
筆者は,看護師を目指す留学生のためのライティング教材の開発を行った。本稿は,開発に至った背景,開発の過程,その内容,想定される使用方法などについて述べる。まず,開発に至った背景については,看護学生・看護師向けのライティング教材を分析し,留学生の日本語教育にそのまま応用することは難しいことを明らかにした。その後,開発の経緯や内容について述べた。看護師と日本語教師が共同で開発にあたり,看護学科で用いられている課題を分析し,その上で必要なものを選んだ。さらに,実際のテキストを示しながら,本書の特徴を述べた。看護実習の流れにそった内容になっており,大きく「実習前」「実習中」「実習後」に分け,形式に関する説明を加え,電子カルテなど実際に看護実習で情報を得るための資源を入れ,ステップアップできる練習問題を豊富に用意した。最後に,想定される使用法や,今後の課題を述べた。
- 著者
- Noritaka Hamano Hitoshi Shitara Tsuyoshi Tajika Tsuyoshi Ichinose Tsuyoshi Sasaki Takuro Kuboi Daisuke Shimoyama Masataka Kamiyama Ryosuke Miyamoto Fumitaka Endo Kurumi Nakase Tsutomu Kobayashi Atsushi Yamamoto Kenji Takagishi Hirotaka Chikuda
- 出版者
- The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine
- 雑誌
- Progress in Rehabilitation Medicine (ISSN:24321354)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.6, pp.20210015, 2021 (Released:2021-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 32
Objectives: We aimed to examine the relationship between the hip range of motion (ROM) and ankle ROM and throwing-related shoulder and elbow injuries in elementary school baseball pitchers.Methods: This retrospective comparative study (Level of evidence: Level III) included 195 baseball pitchers (mean age 10.8±1.0 years, range 8–12 years). All pitchers underwent physical function measurements, including height, weight, shoulder strength, and hip and ankle ROM. Shoulder and elbow injury was defined as shoulder and elbow pain that the pitchers had been aware of in the past or at the time of medical checkups. The results for the injured and non-injured groups were then compared.Results: The shoulder ROM and strength in the injured and non-injured groups did not differ to a statistically significant extent. The hip external rotation on the dominant side (injured vs. non-injured: 48.9±11.1° vs. 53.3±9.7°, P<0.01), the hip internal rotation on the non-dominant side (injured vs. non-injured: 36.6±12.0° vs. 40.9±11.0°, P=0.01), and ankle plantar flexion on the non-dominant side (injured vs. non-injured: 52.0±6.8° vs. 54.3±6.7°, P=0.02) were significantly smaller in the injured group than in the non-injured group.Conclusions: The hip external rotation ROM on the dominant side and the hip internal rotation and ankle plantar flexion on the non-dominant side were significantly lower in the injured group than in the non-injured group. These results may suggest measures to reduce the incidence of elbow and shoulder injuries in elementary school baseball pitchers.