- 著者
- 藤井 範久 小山 陽平 阿江 通良
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.1, pp.17-32, 2010 (Released:2010-07-20)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 3
The purpose of this study was to investigate techniques for accelerating the hammer head in the turn phase of the hammer throw by comparing the motions of hammer throwers. Ten male throwers (PB: 43.15-68.21 m) participated in the study. The hammer motions were videotaped on high-speed VTR cameras (250 or 200 fps), and three-dimensional coordinates were calculated using a DLT method. Various kinematic parameters were calculated, including the hammer head speed, the increase in hammer head speed at each turn phase, the leading distance of the handle (hand), the horizontal abduction/adduction angle of the left arm (shoulder), the twist angle of the trunk, the rotation angle of the pelvis, and the horizontal abduction/adduction angle of the left hip. The fundamental factors and techniques responsible for accelerating the hammer head were as follows: (1) Increasing the acceleration and decreasing the deceleration of the hammer head in the turn phase increased the release speed of the hammer head. (2) A longer positive leading distance of the handle (hand), defined as the distance from the handle to the line connecting the hammer head and the instantaneous center of rotation of the hammer head, had a larger effect on the acceleration of the hammer head in the turn phase. (3) The horizontal abduction of the leading arm (shoulder), the negative trunk twist (recoiling motion), and the sway motion at the midpoint between the two shoulder joints toward the rear and trailing-arm side of the body increased the positive leading distance of the handle by generating the power of the legs and trunk simultaneously.
- 著者
- 木下 秀明
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.51, no.2, pp.151-163, 2006
Michiaki Nagai, the only professor of gymnastics (now known as physical education) at Tokyo Higher Normal School, was the only person who maintained that the aim of <i>kendo</i> (swordsmanship) should be not simply to advance its techniques but to build up spiritual ability through swordsmanship practice, taking the place of <i>gekiken</i>, a part of <i>kenjutsu</i> (swordsmanship), which was hitting practice with a bamboo sword. He first suggested this idea at the first special school for swordsmanship instructors selected from middle schools across Japan, held by the Ministry of Education in 1911. The aim of this article is to clarify when Nagai decided to change the name from <i>gekiken</i> to <i>kendo</i> by researching all of his articles and books describing martial arts, including swordsmanship, published from 1909, when he returned from abroad study, to 1915, when he wrote the foreword for <i>kendo</i>, the first great reference book for instructors, written by S. Takano, the swordsmanship instructor of the School. It is concluded that because Nagai did not have any idea about the name for swordsmanship with a bamboo sword at the beginning of his research, he used <i>gekiken</i> as the subject name for the School. However, he decided to use <i>kendo</i> instead of <i>gekiken</i> in August 1910, when the School adopted <i>kendo</i> as the subject name. As soon as the Ministry adopted <i>gekiken</i> as the official term for the school subject in July 1911, he acted publicly to use <i>kendo</i> for the School, in spite of the decision of the Ministry.
1 0 0 0 OA 中長距離ランナーにおける高強度走行中のステップ変数と走の経済性
- 著者
- 丹治 史弥 榎本 靖士 鍋倉 賢治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.2, pp.523-534, 2017 (Released:2017-12-19)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 2
This study investigated the relationships between running economy and various step parameters (ground contact time, step length and step frequency), as well as the effects of these relationships on differences in foot strike pattern at intensities ranging from below to above the lactate threshold in well-trained distance runners. Thirty-one male distance runners (20 middle-distance and 11 long-distance; age 19.5±1.2 years, height 171.7±4.5 cm, mass 57.6±3.5 kg, BMI 19.5±0.7) participated. Their seasonal best performance was 804.0±121.0 points, expressed as the IAAF score. Both running economy and step parameters were calculated for speeds of 15.0, 16.2 and 17.4 km·h−1, which corresponded to intensities below, equivalent to and above the lactate threshold, i.e. 93.2%±6.4%, 100.6%±6.9% and 108.1%±7.4%, respectively. As running speed increased, running economy, step length and step frequency increased, whereas the ground contact time decreased. A significant positive relationship was observed between ground contact time and running economy at an intensity above the lactate threshold (r=0.46, p<0.01). A significant positive relationship was observed between step length and running economy (r=0.54 and 0.52, p<0.01), and a negative relationship was observed between step frequency and running economy (r=−0.55 and −0.53, p<0.01) at intensities equivalent to and above the lactate threshold, respectively. Middle-foot strikers exhibited a shorter ground contact time than rear-foot strikers at intensities equivalent to and above the lactate threshold, whereas running economy exhibited no significant difference in terms of foot strike pattern. From the present results, it can be concluded that a shorter ground contact time enhances running economy; however, running economy is not related to the foot strike pattern at an intensity of 90%—110% of the lactate threshold.
- 著者
- 森 健一 吉岡 利貢 苅山 靖 尾縣 貢
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.1, pp.275-284, 2012 (Released:2012-06-02)
- 参考文献数
- 37
The purpose of this study was to verify the applicability of the Wingate test (WT) for evaluation of anaerobic capacity and performance in sprinters, based on the relationships among the maximal accumulated oxygen deficit (MAOD) during cycling, accumulated oxygen deficit (AOD-WT), and output power during the WT. Eight 400-m sprinters (SP group; 49.29±1.56 s) and six decathletes (DC group; 50.29±1.27 s) participated. They performed the WT on an electromagnetically braked cycle ergometer. The applied resistance was 7.5% of body weight, and the duration was 60 s. Moreover, anaerobic capacity (MAOD) was determined using a supramaximal constant load test. The oxygen uptake during each test was recorded using the breath-by-breath method. The results were as follows: 1) There was no significant difference between MAOD during cycling and AOD-WT, and a significant correlation between these parameters was evident. 2) In the SP group, there were significant correlations between 400-m performance and MAOD during cycling, and the mean power at 30 s in the WT. However, no significant correlations were observed in the DC group. These results suggest that in sprinters, the applicability of the WT for evaluation of anaerobic capacity and sprint performance differs between cycling exercise and running exercise.
- 著者
- 瀬戸 恵佑
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, pp.260_3, 2016
<p> 現在野球界において効率的なトレーニング方法の研究が数多く行われている。しかし育成年代の野球選手における多くのトレーニングは非効率であり、トレーニング時間も長時間におよぶことが桑田らをはじめとして問題提起されている(2010)。本研究では男子中学生シニアリーグ選手のトレーニング中の移動距離および移動速度と生理学的応答について、携帯型GPS装置、携帯型心拍数計を用いて測定し、トレーニング時間および運動強度を明らかにすることを目的に行った。本研究で得られた主な結果は以下のとおりである。トレーニング時間は8時間であり、トレーニング中の総移動距離は9732 ±434m、トレーニング中の最大速度は19.6 ±3.7km/h、トレーニング中の心拍数は平均126 ± 9拍/分、最大心拍数が170 ± 10拍/分、そして心拍数水準は61 ± 4%であった。また投球練習中と打撃練習中における酸素摂取量、エネルギー消費量、METSの測定も行った。以上のことからシニアリーグにおけるトレーニングは長時間におよび、比較して実際のプレー時間が極めて短い可能性があるため、間欠的トレーニングや少ない時間で効率を重視するようなトレーニングを取り入れていく事が重要であると考えられる。</p>
1 0 0 0 20C20703 帰化選手に対するメディア報道の分析
- 著者
- 千葉 直樹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会号
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, 1999
- 著者
- 松尾 博一 山田 幸雄 増地 克之 松元 剛
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.2, pp.665-677, 2017 (Released:2017-12-19)
- 参考文献数
- 32
The purpose of this study was to verify the effectiveness of the Heads Up Tackling program for defensive players and its influence on safety and performance. Head impacts in football players are directly associated with brain and spine injury, and have been proposed to be associated with injuries such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Therefore, improvement of safety has been a challenge in American football, from the perspective of injury prevention. In 2012, USA Football, the national governing body for amateur American football in the USA developed the Heads Up Football (HUF) program which included “Heads Up Tackling” (HUT), a set of new guidelines for tackling. HUT has been attracting attention in the context of safe tackling through a new coaching methodology. Although in Japan so far, there have been no reports of football-related chronic injuries caused by head impacts, many concussions occur in football games. Therefore, it seem necessary to identify a methodology for teaching tackling techniques in order to reduce the risks of head and neck injury. A number of studies have focused on coaching intervention in relation to safety, and for reducing head impact exposure and injury. However, no reports have focused on the impact of these efforts on athletic performance during a game. If it could be confirmed that HUT reduces the risk of injury in football games without decreasing athlete performances, it would be a useful resource for instruction on tackling skills. Here, 4 matches in the Japan top league (X-league) 2014 and 2015 season were analyzed, before and after HUT intervention was executed in the preseason of 2015. A total of 166 coded tackles were compared in terms of “tackling characteristics”, “amount of injuries”, “effectiveness of tackling”, and “loss of yards” to examine the effect of HUT techniques on “safety” and “effectiveness”. The results revealed that (1) the frequency of “head down” tackling was significantly lower after HUT intervention, (2) the “amount of injuries” was reduced after HUT intervention, (3) there was no effect on the “effectiveness of tackling” in games, (4) “loss of yards” was reduced after HUT intervention, and (5) HUT appeared to reduce the risks of injury in football games, without decreasing tackling performance.
1 0 0 0 OA スキッピングトレーニングが体力, 疾走能力, 疾走動作に与える効果
- 著者
- 尾県 貢 生田 香明 猪熊 真 関岡 康雄 大山 良徳 近藤 潤
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.1, pp.69-78, 1988-06-01 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The skipping is the movement modeled after sprint running. The purpose of this study was to examine effects of skipping training on physical fitness, sprint ability and sprinting form. Nine non-athlete male university students participated in the training consisted of skipping exercises three days per week for eight weeks. The experiment was performed before and after the training period. The experiment was composed of measuring physical fitness and filming 100 m dash. Variables of analysis were: 1) back strength, vertical jump, stepping effeciency while sitting on a chair, 2) maximum anaerobic power, 3) isokinetic peak torque and isokinetic endurance of knee extension and flexion, and hip flexion, 4) 100m sprint record, and sprint record in each 20m sections, 5) running velocity, step frequency and step length, 6) thigh angle and angular velocity, and knee angle and angular velocity, 7) time for one step, support time and nonsupport time, 8) locus of ankle around trochanter major. Results were as follows: 1. Factors of physical fitness such as back strength, maximum anaerobic power and isokinetic peak torque were significantly improved after training. 2. 100m sprint record was significantly shortened, due to the increase of step frequency. 3. After training, the maximum running velocity was kept up for a longer period, and running velocity in 80 m to 100 m became remarkably faster. 4. After training, time for one step and nonsupport time were significantly shortened. 5. The knee lift during recovery phase became significantly higher. 6. The angular velocity of thigh of recovery leg became significantly faster. It is concluded that the skipping training for eight weeks improves sprint ability, sprinting form and physical fitness related to sprint running.
- 著者
- 武田 剛 酒井 紳 高木 英樹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集 第68回(2017) (ISSN:24241946)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.145_2, 2017 (Released:2018-02-15)
競泳競技はスタート台やプール壁をけることで得られる速度が泳ぎ(ストローク動作)よりも高い。この高い速度を維持する目的で、自由形種目では完全水没状態でドルフィンキックやフラッターキックを使用し、ストローク動作(クロール泳)に移行する。競技会において選手が使用するこのキックの種類は、ドルフィンキックのみとドルフィンキック後にフラッターキックを使用するタイプに分けられる。このドルフィンキック後に使用するフラッターキックの影響を明らかにすることを本研究の目的とした。対象はよくトレーニングを積んだ大学生男子競泳選手8名とした。実験参加者にはプール壁からの水中スタート後のキックの種類をドルフィンキック後フラッターキック(試技①)、ドルフィンキックのみ(試技②)の2種類で実施してもらった。選手の水着に自発光型防水LEDマーカーを貼り付け、画像分析法(2次元DLT)によって選手の泳速度を算出した。試技①のフラッターキックの使用によって有意な泳速度の低下が確認され、クロール泳の浮き上がり動作におけるフラッターキックの使用は大きな減速を招くことが明らかとなった。
1 0 0 0 OA 09方−10−口−10 牽引泳中の牽引力のトレーニング成果指標としての活用法
- 著者
- 岸野 力 武田 剛
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集 第68回(2017) (ISSN:24241946)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.211_1, 2017 (Released:2018-02-15)
競泳トレーニングにおいて抵抗体やゴムチューブによる牽引泳をスプリントトレーニングとして導入されるようになってきた。しかしながら実際のトレーニング現場ではチューブでの牽引力を日常的に評価することは少ない。そこで本研究は牽引力とスプリントパフォーマンスの関係性を明らかにし、スプリントトレーニングとしての牽引泳の意義とゴムチューブを介して得られる牽引力のトレーニング指標としての活用法を提案することを目的とした。対象者は日常的に水泳のトレーニングを十分に積む男性15名とした。試技は25mの屋内プール(25m×7レーン 水深1.1~1.2m)にて25mクロール泳タイム測定と牽引泳パワー測定に分けて行った。牽引泳パワー測定は牽引泳8秒と12秒休息×8セットのトレーニング内容で行った。牽引力の計測にはデジタルフォースゲージ(FGPX-100日本電産シンポ社製)にゴムチューブを装着し、クロール泳中の牽引力を測定した。牽引力の最大値、平均値と力積を求め、スプリント泳速度との相関関係を検討した。結果として最大泳速度と最大牽引力との間に有意な相関が認められ、25mの最大泳速度と牽引泳での最大牽引力には高い関係性があることが明らかとなった。
1 0 0 0 OA 09方−10−口−30 競泳選手におけるVR映像がパフォーマンスに及ぼす影響
- 著者
- 林 享 草薙 健太 水上 拓也 松井 健
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集 第68回(2017) (ISSN:24241946)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.217_3, 2017 (Released:2018-02-15)
近年、スポーツ選手の競技力向上を目的として、体力や技術のトレーニングに加えて、精神面のトレーニングとしてのイメージトレーニングが注目されている。最近では、水泳界において、小型防水ビデオカメラを用いることで水中でも主観的な映像からバーチャルリアリティー映像(VR映像)を体験することが可能になり、競泳選手の新しいイメージトレーニングの手法としてVR映像が使用できる可能性が考えられる。以 上のことから、本研究の目的は、競泳選手におけるVR映像が、最大努力泳に及ぼす影響を明らかにすることとした。本実験には、鍛錬された男性競泳選手11名が参加した。被験者はVR映像視聴(VR)とVR映像視聴しない(コントロール)試技を行い、VR試行では視聴直後に100m自由形全力泳を行った。測定項目は、100m泳タイムおよび乳酸値であった。実験の結果、100m泳タイムはVRがコントロール条件より速くなる傾向がみられ、レベルが低い選手ほどタイムの改善が顕著であった。また、乳酸においては、最大値がVRにおいて高くなる傾向にあり、最大値から全力泳後10分後までの減少量も、VRがコントロール条件に比べて有意に大きかった(p<0.05)。
1 0 0 0 OA 09方−10−口−39 水中ドルフィンキックにおけるフィン使用時の動作変化
- 著者
- 野村 美咲 生田 泰志 谷川 哲朗
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集 第68回(2017) (ISSN:24241946)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.220_3, 2017 (Released:2018-02-15)
ドルフィンキック動作で、高い泳速度を得るためには、各関節動作を狭くし身体の振り幅を小さくすることによりストローク頻度を大きくすることが重要である(仁木2013)。練習時にこの動きを習得するためにフィンを使用することが多くある。本研究では、水中ドルフィンキックにおけるフィンの使用による泳パフォーマンス及び身体関節角度の変化を明らかにすることを目的とした。対象は、大学水泳部に所属する男子競泳選手7名、女子競泳選手7名であった。対象者は、15mドルフィンキック泳を最大努力でフィン未使用、フィン使用の計2本実施した。対象者の右側方より水中映像を撮影し、その映像よりキック速度、キック頻度、キック長、キック幅、肩関節角度・腰関節角度・膝関節角度及び足関節角度の最小値及び最大値を求め、フィンの使用前後で比較した。その結果、フィン着用時のキック速度の増加はキック長の増加によること、また、フィン使用時に肩関節及び膝関節の屈曲が少なくなることにより、キック幅が減少したことが明らかとなった。さらに、足関節の過伸展により足先のしなりが生まれたと考えられる。
- 著者
- 久保 正秋
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.5, pp.485-490, 2002
- 被引用文献数
- 1
1 0 0 0 OA 日本におけるスポーツの史的考察 : 明治時代の長距離競走について
- 著者
- 鈴木 正
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.1, pp.254, 1959-09-30 (Released:2016-12-31)
1 0 0 0 IR 水平面における下胴の動きに着目した疾走動作の三次元動力学
- 著者
- 大島 雄治 藤井 範久
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.115-131, 2016
The purpose of this study was to clarify the function of torques exerted by the joints of the lower trunk during maximal velocity sprinting. Eight male track and field athletes volunteered, and sprinted 60 m from a standing start position. The ground reaction force of the support leg was determined using a force platform (1000 Hz), which was placed at the 50-m mark from the start position. Simultaneously, 3D coordinates were recorded with a motion analysis system (250 Hz) using 20 cameras (MX-T20). The joint torques were calculated using inverse dynamics. The contribution of joint torques to the right and left hip joint forces, and the torso joint force, was calculated by a method that simultaneously solves equations of motion for each segment and equations of constraint conditions for adjacent segments connected by a joint. The main results were as follows: (1) During the terminal support phase (80-100% normalized time), the angular velocity of anterior rotation of the pelvis decreased and participants in whom this angular velocity decrease was diminished ran faster (p<0.10). (2) During terminal support, the hip joint adduction torque of the support leg and the anterior rotation torque of the torso joint rotated the pelvis forward. The moment of the right and left hip joint forces rotated the pelvis backward. (3) During terminal support, the hip joint force of the support leg was generated by its hip joint flexion and adduction torque, the hip joint extension torque of the recovery leg, and the anterior rotation torque of the torso joint. In contrast, the hip joint force of the recovery leg was generated by the hip joint flexion and adduction torque of the support leg, and the anterior rotation torque of the torso joint. (4) During terminal support, the hip joint flexion torque exerted by the support leg rotated the pelvis backward. The hip joint adduction torque of the support leg and the anterior rotation torque of the torso joint rotated the pelvis forward. Previous studies showed that the hip flexion torque drives the leg forward from the hip joint extension position. This present study has clarified that the hip joint adduction torque of the support leg and the anterior rotation torque of the torso joint nullify backward rotation of the pelvis due to the hip joint flexion torque exerted by the support leg.Keyword: equation of constraint condition for adjacent segments connected by a joint
1 0 0 0 OA 一流400mランナーにおける体力的特性とレースパターンとの関係
- 著者
- 尾縣 貢 安井 年文 大山〓 圭悟 山崎 一彦 苅部 俊二 高本 恵美 伊藤 穣 森田 正利 関岡 康雄
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 体育学研究 (ISSN:04846710)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.3, pp.422-432, 2000-05-10 (Released:2017-09-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
A study was conducted to examine the relationship between the physical characteristics and race patterns of 400-m running in three elite 400-m runners.The experiments were composed of a physical fitness test and an analysis of 400-m race patterns.Maximal O_2 intake, maximal anaerobic power, isokinetic muscular endurance and isokinetic maximum muscular power were evaluated in a laboratory.Final 400-m races in the Japan Championship and the National Sports Festival were filmed using video cameras, and analyzed to calculate the changes in running speed during the 400-m distance.In accordance with the race analysis results, the three 400-m runners were divided into two types.One was the "even pace"type, which showed a tendency to maintain a higher running speed until the finish of the race.The other was the "first half"type, which showed the highest speed from the start until the 190-m point.The even pace type had a higher maximal O_2 intake and isokinetic muscular endurance of the lower limbs.The first half type was a good record holder over 100-m and 200-m distances.These results indicate that physical characteristics influence the race pattern of 400-m running.
1 0 0 0 11-11-10107-2 ダンス課題学習における実践経験差による教師行動の検討 : グループ学習を活性化させるための教師の関わり方(体育科教育学5,11.体育科教育学,一般研究発表抄録)
- 著者
- 齊藤 南
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, 2008
- 著者
- 入澤 裕樹 川村 卓 岡出 美則 森本 吉謙
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, 2008
- 著者
- 増澤 拓也
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会予稿集 第69回(2018) (ISSN:24241946)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.97_2, 2018 (Released:2019-01-18)
バランス能力を向上させる手法として、2点間に張った平らなロープ上でバランス維持するスラックライントレーニング(SL)と、体幹部の堅牢性を高める体幹トレーニング(CT)が、近年注目を集めている。この両者のトレーニングはいずれもバランス能力の向上を目的としているが、SLは重心位置を動かすことで積極的に安定点を探る制御方法をとり、CTは重心位置を動かさず支持基底面から逸脱させない制御方法をとるため、制御様式が大きく異なる。本研究の目的は、SLおよびCTが姿勢安定性向上に及ぼす効果を明らかにすることである。実験参加者をSL群、CT群および統制(CO)群に配置し、15分間のトレーニングを週2回のペースで合計8回実施した。その訓練前後において重心動揺計とビデオカメラを用い、姿勢安定性の評価・分析をおこなった。分析の結果、SL 群は片・両脚の安定面と不安定面上それぞれで重心動揺が改善され、CT群は両脚時のみ重心動揺が安定化した。
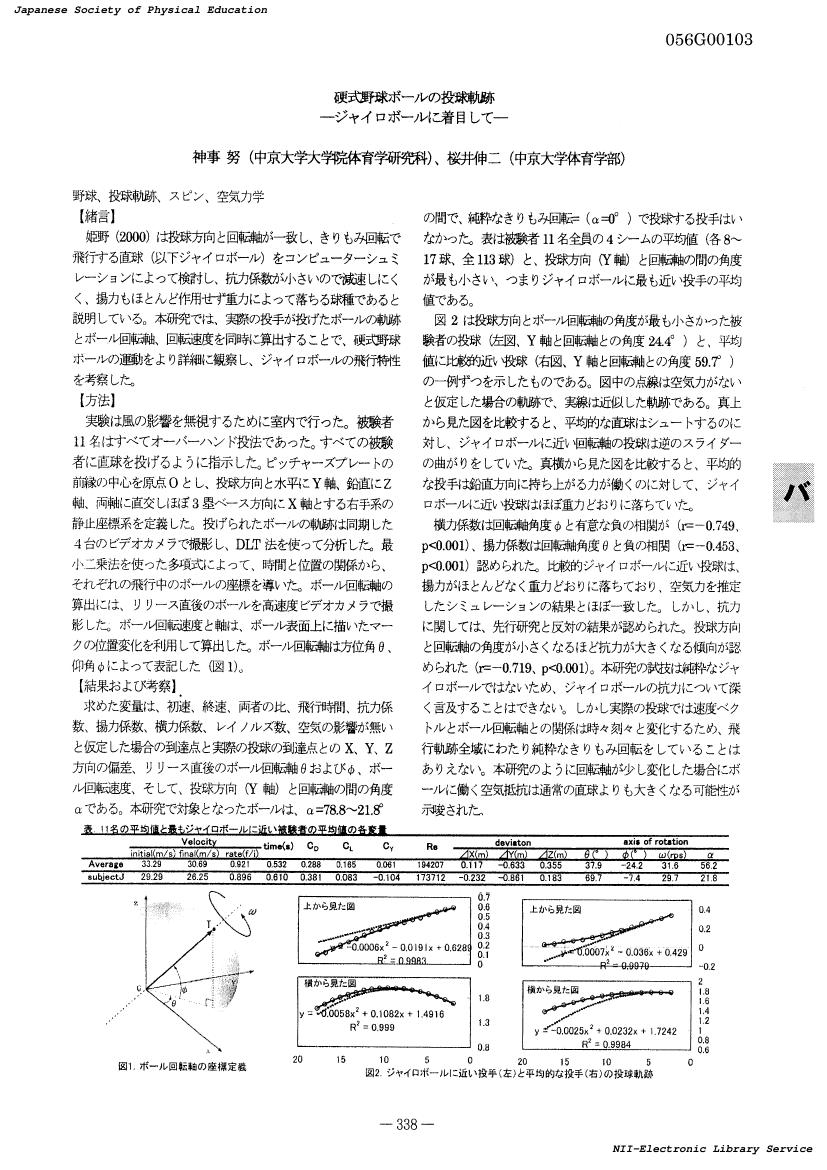
- 著者
- 神事 努 桜井 伸二
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本体育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本体育学会大会号 第55回(2004) (ISSN:24330183)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.338, 2004-09-01 (Released:2017-08-25)