- 著者
- 白柳 洋俊 倉内 慎也 坪田 隆宏
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 土木学会
- 雑誌
- 土木学会論文集D3(土木計画学) (ISSN:21856540)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.75, no.6, pp.I_191-I_197, 2020 (Released:2020-04-08)
- 参考文献数
- 17
本研究は,街並の視覚性ワーキングメモリが注意捕捉を促進するとの仮説を措定し,室内実験により同仮説を検証した.和風型街並を回遊する際,一定時間歩行すると同街並を構成する和風建築要素に対して注意捕捉が促進されることがある.注意捕捉は視覚性ワーキングメモリに保持された視覚的な記憶と類似した要素に対して促進される.そこで本研究は和風型街並を対象に,事前に保持した和風型街並の視覚性ワーキングメモリが駆動することで,事後の和風型街並の和風建築要素に対して注意捕捉の促進が生じるとの仮説を措定し,同仮説を視覚探索課題により検討した.実験の結果,和風型街並を事前に認知することで,事後の和風建築要素に対する注意捕捉が促進すること,すなわち仮説を支持する結果が得られた.
- 著者
- 倉持 清美
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本発達心理学会
- 雑誌
- 発達心理学研究 (ISSN:09159029)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.1, pp.1-8, 1992-09-25 (Released:2017-07-20)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
幼稚園の自由遊び時間に生じた子ども達のいざこざを観察し, いざこざの中で使用される方略が, いざこざ当事者の子ども達の関係によって異なるかどうかを検討した。子ども同士の関係は, 同じ遊び集団に所属しているのか, あるいは異なる遊び集団に所属しているのかどうかで分類した。幼稚園の年長2クラスの5歳から6歳までの42人の子ども達について, 4月から10月までの自由遊び時間にテープレコーダーとフィールドノートを使って週に2〜3回観察して, 37の事例を収集した。同じ遊び集団に属する子ども達の間では, 主に, 物を先取りしていることを主張する方略と, その物を所有することが展開されている遊びにとって必要であること, 例えばお母さん役の子どもが所有することが妥当であることを示す方略を使用した。異なる遊び集団に属する子ども達は, 貸すための条件を示す方略と借りる限度を示す方略を使用した。この結果は, 子ども達がいざこざの中で使用する方略が子ども達同士の関係の違いによって選択されていることを示した。
- 著者
- 谷尾 崇 倉本 宣
- 出版者
- 日本鱗翅学会
- 雑誌
- 蝶と蛾 (ISSN:00240974)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.2, pp.59-63, 2019-08-31 (Released:2019-09-12)
- 参考文献数
- 21
In order to investigate the time of initiation of post-diapause development, we reared diapausing larvae of introduced Hestina assimilis assimilis and native H. persimilis japonica, with a photoperiod of 14L-10D under four regimes of constant temperatures (15.0℃, 17.5℃, 20.0℃ and 22.5℃) and one regime of increasing temperature (10.0℃- 28.0℃). On the lowest temperature regime, the larvae of H. a. assimilis awoke slightly earlier than those of H. p. japonica. On the increasing temperature regime, the larvae of H. a. assimilis awoke from 12℃ and showed many individual differences, while those of H. p. japonica awoke from 14℃ with limited individual differences. The larvae of H. a. assimilis probably secure and dominate food resources more quickly and have a higher adaptability to spring climates. Hestina a. assimilis may have spread its distribution range in Japan due to the above factors.
1 0 0 0 OA 江戸時代に於ける蝦夷地移民論
- 著者
- 高倉 新一郎
- 出版者
- 北海道帝國大學法經會
- 雑誌
- 北海道帝國大學法經會法經會論叢 (ISSN:03855961)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, pp.22-35, 1936-01
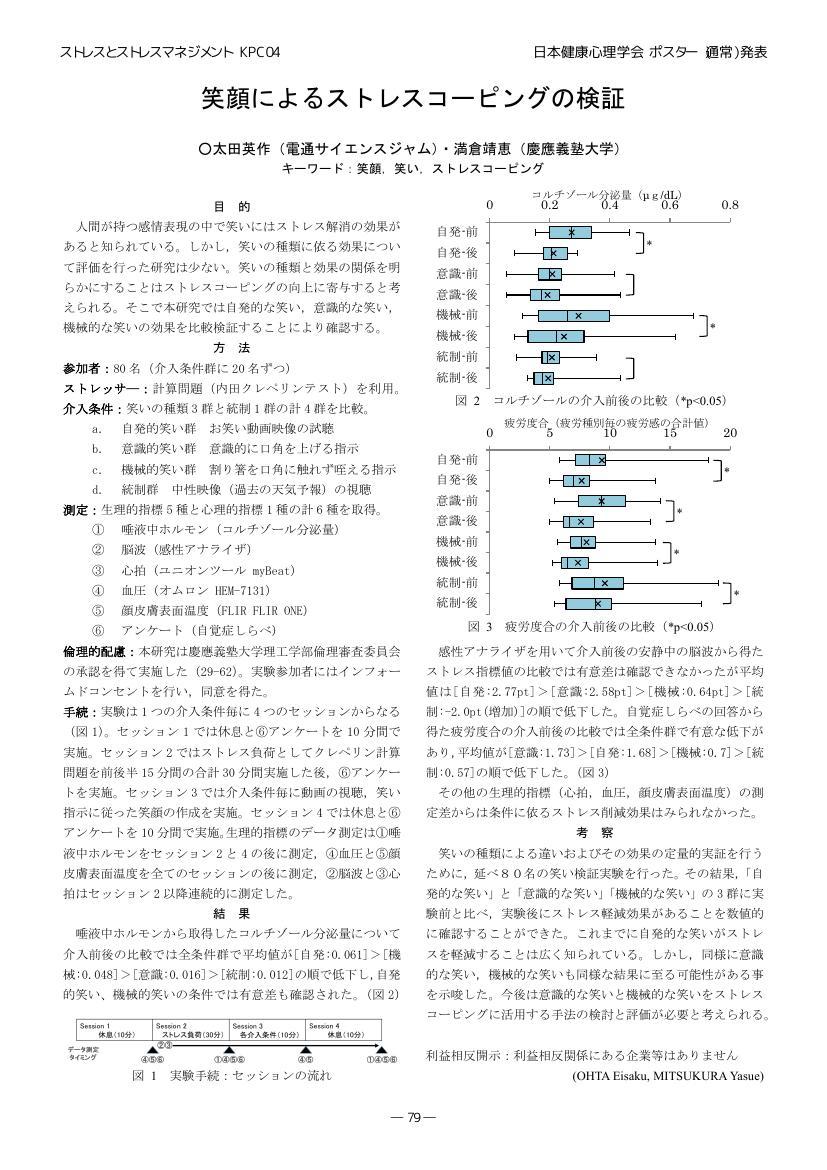
1 0 0 0 OA 笑顔によるストレスコーピングの検証
- 著者
- 太田 英作 満倉 靖恵
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本健康心理学会
- 雑誌
- 日本健康心理学会大会発表論文集 31 (ISSN:21898812)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.P79, 2018 (Released:2018-08-14)
1 0 0 0 OA アメリカの表現強制の法理と表現の自由
- 著者
- 岩倉 秀樹
- 出版者
- 高知県立大学文化学部
- 雑誌
- 高知県立大学文化論叢 (ISSN:21876673)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, pp.37-60, 2015-03-31
1 0 0 0 OA 粘土を用いた芸術療法的アプローチを行う際の留意点
20世紀半ばにその名前が登場した芸術療法の技法は多様であるが、その中に粘土を用いた造形活動もある。粘土は立体的な表現が可能で、可塑性が高い、多くの人が幼児期に使ったことがあるなどの特徴を生かした利用をされている。本研究では、このような粘土造形を行った際の心理状態を数量的データにより調査することを目的とする。そのために、一般大学生40名を対象に粘土造形を試行させて、粘土に触った感想と制作物の題名を調査した。結果は、感想からは「手触り」や「素材の特徴」など10個のカテゴリ、作品の題目からは「動物」や「キャラクター」など7個のカテゴリが得られた。この結果から、粘土を扱うとその手触りから退行が促進され、癒しの効果が得られることが明らかになった。そして、粘土を触った感想は、思考、感覚、感情という3つのレベルから考えられることも分かった。また、柔らかさを中心に手触りについての感想が多かった。さらに、粘土の使用はコミュニケーションツールにもなると考えられ、グループワークへの活用も期待できる。
1 0 0 0 OA 調理時におけるライフサイクルCO2排出量の実践的定量
- 著者
- 津田 淑江 大家 千恵子 瀬戸 美江 久保倉 寛子 稲葉 敦
- 出版者
- 日本LCA学会
- 雑誌
- 日本LCA学会誌 (ISSN:18802761)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.3, pp.288-297, 2006 (Released:2007-09-20)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 5 3
The study examined the volume of Life Cycle CO2 emission from Japanese, Western and Chinese dishes that are daily consumed by the Japanese, especially it compared the volume of CO2 emission depending upon a different cooking process. The results of the analysis revealed as follows. 1. CO2 emission is greatly influenced by the purchase of in-season product and the use of food ingredients produced in nearby prefecture. 2. It is clear that the size of cooking pot, adjustment of cooking temperature, whether or not to use a pot cover while cooking could affect on the reduction of CO2 emission. It is necessary to devise suitable cooking process for CO2 emission reduction because CO2 emission could be increased depending on certain cooking process such as boiled or steamed. The volume of CO2 discharged from cooking by one household is limited; however it becomes larger when taking the total number of Japanese households into account. (49,530,000 according to 2005 census) It is evident that every household should concern on CO2 emission from cooking since it could reduce the environmental burdens.
1 0 0 0 発作時にくしゃみを伴った異型狭心症の1例
- 著者
- 居倉 博彦 児玉 光司 池田 俊太郎 橋田 英俊 桑原 大志 岡山 英樹 原 裕二 重松 裕二 小原 克彦 濱田 希臣 日和田 邦男 藤原 康史
- 出版者
- 医学書院
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.619-622, 1997-06-15
症例は47歳,男性.1995年4月22日午前7時頃,くしゃみをした直後に前胸部圧迫感が出現した.痛みは約15分続いた.さらに,同年5月16日午前7時頃,くしゃみをした直後に前胸部圧迫感が生じた.その際,便意も催し,排便後に失神したが,意識は10分弱で同復し,胸痛も消失した.近医の紹介により同年5月29日に当院に入院した.6月1日に冠動脈造影検査を施行,コントロール造影では両側冠動脈に器質的狭窄を認めなかったためアセチルコリン冠攣縮誘発試験を行った.その結果,右冠動脈,および左回旋枝は完全閉塞し,それに伴って胸部圧迫感と心電図上ST上昇を認めた.以上より異型狭心症と診断した.以後,抗狭心症薬の投与により狭心症発作は一度も起きていない.本症例は狭心症発作の前駆症状にくしゃみを認めた稀な症例である.
- 著者
- 小倉 仁志
- 出版者
- 日経BP社
- 雑誌
- 日経情報ストラテジ- (ISSN:09175342)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.8, pp.110-112, 2011-09
ナゼナゼ社の営業部にて。ミツオさんとチエさんが言い合いをしている。「ミツオさんは業務の不完全なところにはまりやすいのよね」「チエさんだってお客様の名前を間違えたことがあったじゃないですか。確かに今回のミスは、チェックしなかった自分のせいではあるけれど」。実はミツオさん、2日前にロジック社に見積書を送ったのだが、間違いが発覚した。
1 0 0 0 検査用グミゼリーを用いた咀嚼能率検査法の改良
1 0 0 0 歯科医院における有床義歯装着者の咀嚼能率に影響を及ぼす要因
1 0 0 0 一般歯科医院における患者の咀嚼能率に影響を及ぼす要因
1 0 0 0 OA 一九五〇年代後半の米国軍縮・軍備管理政策と同盟関係-ドイツ再統一との連関を巡って-
- 著者
- 倉科 一希
- 出版者
- JAPAN ASSOCIATION OF INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
- 雑誌
- 国際政治 (ISSN:04542215)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2003, no.134, pp.42-55,L9, 2003-11-29 (Released:2010-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 67
This article discusses the development of the Junktim between East-West disarmament/arms control negotiations and German reunification and the changes in American policies regarding the Junktim under the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower. It argues that the United States government at that time changed the Junktim in order to make current disarmament negotiations with the Soviet Union possible. At the same time, the Eisenhower administration did not enforce the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) to abandon the latter's objection to the issues relating to European security and to accept the US policy changes in these matters.The Junktim was established as a US policy and as a common Western policy in 1955-56. The Eisenhower administration had inherited a policy of the Junktim from the previous administration. Discussions about US disarmament/arms control policies before and after the Geneva four-power summit meeting in July 1955 reconfirmed this policy with the support of all major members of the administration, including Harold E. Stassen, Special Assistant to the President for Disarmament. The major Western allies had agreed to a Junktim between European security and German reunification before the Geneva summit meeting, but the British, the French and the West Germans soon found themselves divided regarding the definition of this Junktim. US efforts to close the gap among Europeans led to agree another Junktim between German reunification and arms reduction by stages as an allied position in May 1956.The Eisenhower administration tried to change the Junktim in order to widen the range of discussions with the Soviets. First, Stassen tried to define the first stage of an arms reduction proposal which would be implemented without progress toward German reunification. After Stassen's failure in 1957 and departure in the next year, Secretary of State John Foster Dulles opened a way to negotiate a nuclear test ban treaty with the Soviets and the British without discussing German reunification. After a Soviet ultimatum on Berlin in November 1958, President Eisenhower and the newly appointed Secretary of State, Christian A. Herter, connected nuclear test ban negotiations with Berlin negotiations in order to improve prospects of the latter.These US efforts upset Bonn, but Washington did not totally neglect Bonn's concerns. First, Washington modified the Junktim but did not abandon its principle. Second, Bonn's objection against accepting European security measures without progress toward reunification was recognized by the Eisenhower administration.Washington's effort to modify the Junktim indicates its willingness to negotiate with the Soviets and its desire not to destroy the alliance with the FRG. This study shows the second half of the 1950s as a dynamic period of the Cold War and gives a hint that can explain the developments in the following decades.
1 0 0 0 OA サイトメガロウイルス関連血球貪食症候群および肺炎を併発した全身性エリテマトーデス
- 著者
- 田中 康博 瀬尾 龍太郎 永井 雄也 森 美奈子 戸上 勝仁 藤田 晴之 倉田 雅之 松下 章子 前田 明則 永井 謙一 小谷 宏行 高橋 隆幸
- 出版者
- 日本臨床免疫学会
- 雑誌
- 日本臨床免疫学会会誌 (ISSN:09114300)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.1, pp.71-75, 2008 (Released:2008-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2
症例は58歳の女性.31歳より全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)および抗リン脂質抗体症候群(APS)のためprednisoloneとazathioprineを内服しSLEとAPSは安定していた.2004年10月,発熱を伴う感冒様症状が出現したので近医に入院.抗生剤は無効で血小板減少が出現したので,SLEの増悪との診断のもとステロイドパルス療法が施行された.しかし,汎血球減少へと進展したので当院へ転院となった.骨髄穿刺で血球貪食像が認められ,胸部CTで肺門部を中心とするスリガラス影が認められた.同日のcytomegalovirus (CMV) antigenemiaが陽性であった.以上より,CMV関連血球貪食症候群(hemophagocytic syndrome ; HPS)およびCMV肺炎と診断.azathioprineを中止しprednisoloneを減量してgancyclovirを開始.これにより解熱し汎血球減少は改善した.現在,外来通院中でCMV感染の再発を認めていない.SLEなどの膠原病にCMV関連HPSを併発することは稀であるため報告する.
- 著者
- 藤倉 雄二
- 出版者
- COSMIC
- 雑誌
- 呼吸臨床 (ISSN:24333778)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.5, pp.e00031, 2018 (Released:2020-10-22)
- 参考文献数
- 21
1918年から流行したスペインインフルエンザでは,全世界で4000万〜5000万人が死亡したとされる。当時の資料をみると,特に1918年後半からの流行では致死率が高く,肺炎による死亡が顕著であった。短期間で世界中に拡散し,世界中で多くの被害をもたらしたインフルエンザウイルスは,現代においてreverse geneticsの手法により復元され,多くの知見をもたらしている。
1 0 0 0 OA 類題三河歌集(近世後期類題歌集調査九)
- 著者
- 朝倉 治彦
- 出版者
- 四日市大学
- 雑誌
- 四日市大学論集 (ISSN:13405543)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.1, pp.190-171, 2011 (Released:2020-09-10)
1 0 0 0 OA 失語症者のジェスチャー能力に関する1考察
- 著者
- 藤田 邦子 石川 裕治 中谷 基 熊倉 勇美
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Logopedics and Phoniatrics
- 雑誌
- 音声言語医学 (ISSN:00302813)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.1, pp.14-20, 1993-01-20 (Released:2010-06-22)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 1
失語症患者のジェスチャー表出能力の客観的な評価の試みとして, 表出されたジェスチャーを「構成要素」という考え方を用いて新たに分類し, 「構成要素の数」とその「内容の正確さ」という両側面から評価, 分析した.その結果, (1) 失語群は健常者群に比べ, 構成要素総数の有意な低下がみられた. (2) 失語症が重篤になるに従って, 構成要素総数も少なく, 絵カードに描かれているとおりの形態を2次元的に描くのみで動作を示さないことが多かった.これらは失語症のタイプとは関係なく観察された. (3) 質的分析の結果, 重度失語症例では描いた形態の大きさや正確さが不適切であり, さらにファンクションの数, 質ともに低く, 伝達性の低いことが確認された. (4) 非流暢性タイプの失語症者はジェスチャー伝達に停滞を示すことが多かった.以上の所見に若干の考察を加えた.
- 著者
- 熊倉 俊郎 早川 典生 細山田 得三 播磨 隆
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 土木学会
- 雑誌
- 地球環境シンポジウム講演集
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, pp.147-152, 1996
Numerical simulation by Modular Ocean Model2 (MOM2) is carried out to understand whole image of oceanic structure in the Japan Sea. MOM2 is the numerical simulation code which integrates governing equation and calculates development of momentum, temperature, and salinity. The study is successful to reproduce the flow pattern of oceanic circulation in the Japan sea, which includes meandering of Tsushima Warm Current and the polar front in the center of Japan Sea.