1 0 0 0 OA 動物医療におけるCT撮影時のCT室内散乱線分布と介助者の被ばく量の推定
- 著者
- 森岡 真也 鈴木 敏和 吉田 均 上野 博史 宇塚 雄次
- 出版者
- 動物臨床医学会
- 雑誌
- 動物臨床医学 (ISSN:13446991)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, no.3, pp.95-101, 2018-09-25 (Released:2019-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
人の医療ではCT室内の散乱線量や散乱線分布に関する報告は数多くあるが,動物医療におけるCT撮影時の具体的な散乱線量の調査は見当たらない。そこで今回,動物病院におけるCT検査時のCT室内の散乱線量を測定した。実際の臨床現場で使用する撮影条件を用いてCT室内の散乱線空間マッピングを,頭部・胸部・腹部・骨盤撮影ごとに作成した。マッピングの測定は,床からの高さは50,100,150,200 cmの4平面で行い,全260箇所で行なった。その結果,骨盤撮影時のガントリー中心から尾側50 cm離れた寝台上で最大の133 μSvの散乱線量が記録された。また,床からの高さ100 cmが最も散乱線が大きく,次いで150,50,200 cmの順に小さくなった。ガントリー脇は最も散乱線量が小さいエリアとなった。ガントリーの100 cm四方は散乱線量が大きく,寝台から離れるに従って小さくなった。
1 0 0 0 医療用電磁波場の細胞増殖ならびに遺伝子発現への影響
各種磁場(0.2T均一定常磁場、0.45Tの不均一定常磁場、0.2Tの変動磁場)の細胞への影響を細胞増殖、細胞致死、熱ショック蛋白質および癌遺伝子発現を指標に明らかにした。0.2Tの均一定常磁場を培養器内で1ー8日間HeLaS3細胞(ヒト子宮癌)に負荷しても細胞増殖に影響を与えなかった。放射線(6Gy)あるいは温熱(45C,15min)の併用処置についても変化を認めなかった。0.2Tの変動磁場、0.45Tの不均一定常磁場を室内で1、2時間SCCVII細胞(マウス扁平上皮癌)、HeLaS3細胞に負荷しても細胞増殖、細胞致死いずれも影響を認めなかった。放射線あるいは温熱の併用についても変化を認めなかった。0.2Tの均一定常磁場のHeLaS3細胞での癌遺伝子(Nーras,mycおよびfosを検討)への影響をNorthern blotting法で評価した。無処置対照においては、fosmRNAの産生はほとんど認められなかった。2、8時間の磁場負荷では認められなかった。fosmRNAの産性が、4時間の磁場負荷で軽度認められた。既に報告されているようにfosはTPA、温熱処置にて発現したが、それらの発現に磁場は影響を与えなかった。NーrasおよびmycのmRNA発現に磁場は関与しなかった。ヒト大腸癌由来COLO細胞を対象に0.2T均一定常磁場の熱ショック蛋白質発現への影響をSDSーPAGEで検討したが、6、24時間磁場を負荷しても熱ショック蛋白質の発現を認めなかった。以上、0.2Tの均一定常磁場にてfosmRNAの産性が軽度認められることが本研究で明らかにされた。磁場と癌遺伝子発現の関係についての報告は皆無に等しく今後の研究が望まれる。
- 著者
- 吉岡 真治 町 光二郎 長田 裕也
- 雑誌
- 2023年度 人工知能学会全国大会(第37回)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2023-04-06
1 0 0 0 OA 社会的ミッションをもったコーヒーロースター ――オレゴン州ポートランドの事例から
- 著者
- 畑山 要介 寺島 拓幸 藤岡 真之 野尻 洋平 畑山 直子 ハタヤマ ヨウスケ テラシマ タクユキ フジオカ マサユキ ノジリ ヨウヘイ ハタヤマ ナオコ Yosuke HATAYAMA Takuyuki TERASHIMA Masayuki FUJIOKA Yohei NOJIRI Naoko HATAYAMA
- 雑誌
- 雲雀野 = The lark hill
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.44, pp.33-52, 2022-03-31
1 0 0 0 OA ZDDを用いた集合分割の列挙索引化手法の提案と実験的評価
- 著者
- 高橋 翔哉 吉岡 真治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 人工知能学会
- 雑誌
- 人工知能学会研究会資料 人工知能基本問題研究会 112回 (2020/3) (ISSN:24364584)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.08, 2020-03-01 (Released:2021-07-01)
1 0 0 0 OA 重層化する記憶の場 〈牡丹社事件〉コメモレイションの通時的考察
- 著者
- 宮岡 真央子
- 出版者
- 日本文化人類学会
- 雑誌
- 文化人類学 (ISSN:13490648)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.2, pp.266-283, 2016 (Released:2018-02-23)
- 参考文献数
- 53
- 被引用文献数
- 2
本稿の目的は、外来政権により脱植民地化が代行され、重層化する植民地経験を有する社会にお いて、記憶とコメモレイション(=記憶の共有化)をめぐって先住民が抱える困難について論じる ことである。台湾の先住民である原住民族が初めて日本の植民地主義と邂逅した歴史的事件〈牡丹 社事件〉をめぐる記憶の場では、多様な主体によるコメモレイションがおこなわれてきた。しかし、 原住民族であり事件の一方の当事者である牡丹郷パイワンは近年までここから排除され、彼らにつ いての暴力的・侮蔑的表現は一貫して不問に付されてきた。ゆえに牡丹郷パイワンは、自らの土地 に〈牡丹社事件〉をめぐる新たな記憶の場を創出し、従来抑圧・凍結・等閑視されてきた自らの記 憶と歴史認識を表現し、統治者が流布した牡丹郷パイワンについての固定観念を払拭しようとした。 牡丹郷パイワンによる〈牡丹社事件〉のコメモレイションの一部が文字という記憶の方法でおこな われたことの背後には、中華文明圏における文字の拘束性を看取できる。また、日本の植民地主義 に起源するモニュメントや制度の一部は、今日まで原住民族にとって民族と文化の絶滅の危機の原 点として意味をもち、克服すべき・乗り越えるべき対象としてとらえられている。原住民族による 新たな記憶の場の創出とコメモレイションの背景には、重層化した植民地経験を有する社会におい て、彼らが今日までマイノリティであり被支配的立場にあるという先住民としての現実が横たわる。 原住民族の記憶の抑圧・凍結・等閑視は、2つの外来権力と多数派の漢系住民によって近年まで続 けられてきた。記憶とコメモレイションをめぐるこのような困難は、外来政権が脱植民地化を代行 し、重層化した植民地経験を有する社会において、先住民が向き合うことを余儀なくされている問 題である。
1 0 0 0 OA 二月革命期におけるブルツクスの土地改革論
- 著者
- 森岡 真史
- 出版者
- ロシア・東欧学会
- 雑誌
- ロシア・東欧研究 (ISSN:13486497)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2007, no.36, pp.159-172, 2007 (Released:2010-05-31)
Just after the February Revolution in 1917 Boris Brutzkus actively participated into the public debate over the agrarian reform. This paper shows how he conceived the task of reform under the newborn democratic government. Although his view on this problem is less known than his famous lecture on Marxist socialist economy in 1920, it deserves attention for its unique perspective placing the peasant farming as a vital element in capitalistic development of the Russian economy. His focus of criticism in this period was Russian Populists (Narodniki) who were at that time in the midst of popularity. He strongly warned that their agitation about the overall land distribution without compensation and redemption would not only lead sweeping economic catastrophe but also seriously endanger the fate of democracy.While Populists see the root of agrarian crisis in the land shortage among peasants, Brutzkus points out that the essence of the land shortage was accumulation of agrarian overpopulation caused by the extremely sluggish pace of Russian economic growth. Because of this, Russian industry could neither absorb the increase of rural population nor provide domestic market for agricultural products. In addition, on the side of villages the communal ownership of land held back the population flow into cities. Thus the solution of agrarian crisis needs also the development of industrial production. In his opinion such a development is possible only under capitalism. Therefore the land reform must be compatible with the general framework of capitalist economy. In this connection Brutzkus emphasizes the importance to preserve Stolypin's legislations with necessary democratic revisions. Referring to the experiences of Western countries, he advocates that the peasant's private ownership of land with the system of well-organized mortgage credit can promote intensification of peasant farming and flow of rural surplus population into cities. Since land is now one of precious assets of people, every peasant who receives land must bear responsibility to the national economy for its adequate utilization through the payment of rent corresponding to the prices of expropriated land. From these considerations Brutzkus urges intellectuals to tell people honestly that land cannot be distributed freely. He believes that the success of land reform depends on peasant's individual initiative and energy and for this end the immense energy of excited people must be transformed into creative force for economic construction.Brutzkus' standpoint was similar with those of Neo-populists (Neonarodniki) in its recognition of peasant farming's vitality and deep concern on the fate of national economy. However, Neo-populists still shared with traditional Populists negative attitude toward capitalism and the private land ownership. Most of Russian liberals were also sympathetic to the socialization of land in a moderate form. These circumstances placed Brutzkus in a quite isolated position. The Populist program was adopted by Bolsheviks and put into execution by communal peasants. In this point the October Revolution was the Populist agrarian revolution. Along with his critique of Marxist socialism, Brutzkus' penetrating criticism against Populism has great historical significance in its deep insight and civil bravery.
1 0 0 0 OA 初期ネップ下の提言にみるブルツクスの経済発展観
- 著者
- 森岡 真史
- 出版者
- ロシア・東欧学会
- 雑誌
- ロシア・東欧研究 (ISSN:13486497)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2003, no.32, pp.162-174, 2003 (Released:2010-05-31)
Boris Brutzkus is well-known for his pioneering and penetrating criticism against the Socialist economy. However, relatively less known is the fact that he defended the social role of government to protect the interest of the people. The purpose of this paper is to reconstruct and appreciate his vision of economic development underlying such a unique standpoint.For this purpose Brutzkus's following two important contributions will be investigated: i) his report “Economic Precondition for the Reconstruction of Agriculture” made at the All Russian Congress of Agronomists held in March 1922; ii) his paper “Agrarian Overpopulation and Agrarian Institution” published in the organ of the People's Commissariat of Agriculture in June/July 1922. Both of them include profound insight into the causes of catastrophic destruction of Russian agriculture after the October Revolution as well as several important policy proposals for its restoration.Brutzkus attributes the root cause of agrarian catastrophe to the “black redistribution” and emphasizes that it is not only the Soviet government but also all of the intellectuals and the people who must free themselves from the illusionary idea that the agrarian problem can be solved by nationwide land redistribution. Fully recognizing the limits of NEP as partial liberalization under the Communist dictatorship, he supports the basic direction of NEP for the reason that it serves the interest of Russian national economy.In his schema of national economy, the dynamic agro-industrial linkage, especially the smooth flow of labor from agriculture to urban industry constitutes one of the essential factors in the process of economic development. Coupled with slowness of industrialization, Russian land community hindered this flow of population and became the hotbed of agrarian overpopulation. Agrarian policies and agrarian institutions must be favorable for such a flow and at the same time soften the pain attendant on it. From this follows the necessity of guaranteeing peasants the right to dispose of their land freely. Owing to some fundamental differences between agriculture and industry, this right brings not the victory of agrarian capitalism but promotes the growth of peasant economies and their adaptation to the market environment.For Brutzkus, the national economy is a huge social framework giving its members economic and cultural wealth that they cannot produce alone. Flowering of individual freedom needs development of the national economy. The reason he affirms capitalism and rejects Marxian Socialism is that he firmly believes that the development of national economy in the industrialization era is possible only under capitalism and that individual freedom is inseparable from the private ownership of the means of production. However, as is shown in his argument of the relative advantage of peasant economy in agriculture, dominance of capitalism is neither exclusive nor unconditional even in the market. His vision of the desirable national economy can be characterized by it compositeness and variety created by the mixture both of capitalist institutions playing the leading part and of various kinds of non-capitalist institutions playing secondary but often essential roles.The above-described Brutzkus's vision is highly suggestive in its rare combination of economic logic and due attention to historical factors. Understanding of this vision will be of considerable help in an in-depth appraisal of his critical analysis on the Soviet economy.
1 0 0 0 OA 迷走神経由来の後縦隔ancient schwannomaの1例
- 著者
- 蜂須賀 康己 藤岡 真治 魚本 昌志
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本呼吸器外科学会
- 雑誌
- 日本呼吸器外科学会雑誌 (ISSN:09190945)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.6, pp.633-638, 2022-09-15 (Released:2022-09-15)
- 参考文献数
- 12
症例は48歳,男性.健康診断の胸部単純X線写真で異常影を指摘され当院を受診した.造影CTで左後縦隔に被膜を有する5.5×5.3×5.0 cmの腫瘤を認めた.良性囊胞性腫瘍を疑い切除術を行った.術中所見で腫瘍は胸腔内迷走神経由来であった.病理検査の結果,高度な囊胞変性を伴ったancient schwannomaと診断した.迷走神経由来の後縦隔ancient schwannomaのまれな1例を経験した.
1 0 0 0 OA 人工血液 ~外傷治療における明日にかける橋~
- 著者
- 木下 学 萩沢 康介 石田 治 齋藤 大蔵 酒井 宏水 武岡 真司
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本外傷学会
- 雑誌
- 日本外傷学会雑誌 (ISSN:13406264)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.35.4_05, (Released:2021-10-07)
- 参考文献数
- 36
私たちは止血能と酸素運搬能を有し, 血液型に関係なく投与できる人工血液を研究開発している. 人工血液は人工血小板と人工赤血球から成り, 室温静置で長期保存可能で, 備蓄や病院前治療に適していると考える. 人工血小板はリポソームに血小板活性化因子であるアデノシン二リン酸 (ADP) を内包し, 表面に人工的に合成したフィブリノーゲンの活性部位を付着させている. 出血部位に集積し, 血小板血栓形成を促進することで, 血小板減少性の易出血病態でも血小板と同様の止血能を発揮する. 人工赤血球は使用期限の切れた輸血用赤血球からヘモグロビンを精製し, 同様にリポソームに内包したもので, 優れた酸素運搬能を有している. 人工血液は血小板減少による凝固障害を呈した家兎の致死性出血モデルにおいて, 通常の血小板と赤血球の輸血に匹敵する顕著な止血救命効果が認められ, 外傷治療における有用性が期待される.
1 0 0 0 OA 現代中東の「ワタン(祖国)」的心性をめぐる表象文化の発展的研究
- 著者
- 岡 真理 宮下 遼 山本 薫 石川 清子 藤元 優子 福田 義昭 鵜戸 聡 田浪 亜央江 中村 菜穂 前田 君江 鈴木 珠里 石井 啓一郎 徳原 靖浩 細田 和江 磯部 加代子 岡崎 弘樹 鈴木 克己 栗原 俊秀 竹田 敏之
- 出版者
- 京都大学
- 雑誌
- 基盤研究(B)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2015-04-01
アラビア語、ペルシア語、トルコ語、ヘブライ語など中東の諸言語で、中東地域で生産される作品のみならず、中東に歴史的出自を持つ者によって、欧米など地理的中東世界を超えた地域で、英語、仏語、独語、伊語などの西洋の諸言語で生み出される作品をも対象に、文学や映画などさまざまなテクストに現れた「ワタン(祖国)」表象の超域的な分析を通して、「ワタン」を軸に、近現代中東世界の社会的・歴史的ありようとそのダイナミズムの一端と、国民国家や言語文化の境界を越えた共通性および各国・各地域の固有性を明らかにすると同時に、近現代中東の人々の経験を、人間にとって祖国とは何かという普遍的問いに対する一つの応答として提示した。
1 0 0 0 骨髄幹細胞の自己治癒能と全身の恒常性維持による健康寿命延長
これまでの研究から、老化により生体内のMSCが機能低下(stem cell failure)を起こすことが、個体の老化の原因となっていると考えており、本研究で、MSCの投与・補充による“抗加齢効果”をもたらす詳細なメカニズムを解析し、健康寿命の延長をもたらす治療薬の開発に展開することができると考えている。本研究の成果により、老化の本質が明らかとなり、健康寿命の延長が可能となれば、超高齢化社会を迎えているわが国において、大きな福音となり、波及効果は極めて高いと思われる。
1 0 0 0 OA 脳腫瘍術後の陳旧性眼球運動障害に対する視能訓練
- 著者
- 岡 真由美 深井 小久子 木村 久 向野 和雄
- 出版者
- JAPANESE ASSOCIATION OF CERTIFIED ORTHOPTISTS
- 雑誌
- 日本視能訓練士協会誌 (ISSN:03875172)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.27, pp.139-144, 1999-07-25 (Released:2009-10-29)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Intensive orthopticsにより良好な結果を得た陳旧性の後天性眼球運動障害例の治療経過と視能矯正管理の方法について報告した。症例は33歳の男性で、主訴は複視と動揺視である。第4脳室周囲上衣腫の摘出後に眼球運動障害、複視、眼振が出現した。約2年後、当科に入院し40日間視能訓練を施行した。退院後、北里大学病院眼科で眼振に対する治療を開始した。視能訓練の効果は、斜視角の改善率、融像能率、日常生活上の不自由度で判定した。治療前は融像衰弱(融像能率0%)であった。眼位は9Δ内斜位と右眼2Δ上斜位斜視で輻湊不全と眼振を伴っており、核上、核間、核下性眼球運動障害を示した。視能訓練は、Visual orientation trainingとConvergence trainingを行った。訓練8日目には輻湊近点の改善が認められ、融像能率は66%、改善率は82%になった(第I期)。訓練9日目よりFusion lock trainingを行い、訓練40日目に融像能率は78%になった(第II期)。退院後はSG fusion trainingと眼振治療を行った。訓練1年目に動揺視は軽減し、融像能率が100%、改善率が92%になった(第III期)。不自由度は訓練前100点から訓練後22点に回復した。本例において視能訓練が奏効したポイントは、斜視角が小さいこと、融像衰弱であったこと、患者の訓練意欲にあると考えた。
1 0 0 0 OA 麻痺性斜視における融像状態別の視能訓練成績
- 著者
- 星原 徳子 岡 真由美 河原 正明
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本視能訓練士協会
- 雑誌
- 日本視能訓練士協会誌 (ISSN:03875172)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, pp.229-235, 2016 (Released:2017-02-28)
- 参考文献数
- 24
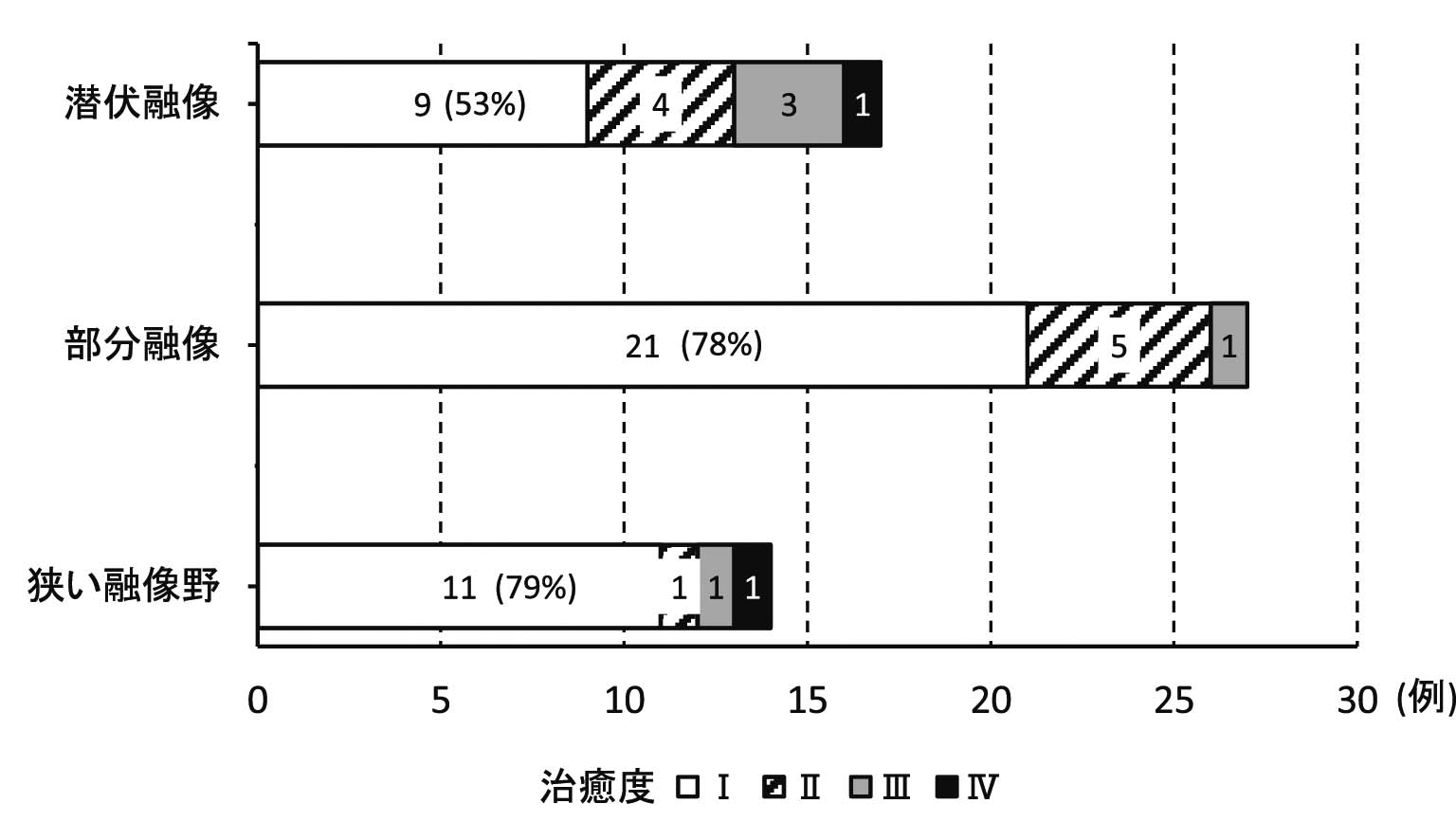
【目的】麻痺性斜視における融像の異常な状態(融像状態)別の視能訓練成績を分析し、家庭訓練を中心とした視能訓練方法を検討した。【対象および方法】対象は、視能訓練を施行した麻痺性斜視58例で、年齢は30~87歳であった。融像状態は、潜伏融像、部分融像、狭い融像野に分類した。視能訓練は、衝動性眼球運動訓練、輻湊訓練、fusion lock training、プリズム療法を行った。治癒度は4段階とし、治癒度Ⅰは融像野が30°以上とした。【結果】融像状態は、潜伏融像27例、部分融像27例、狭い融像野14例であった。治癒度Ⅰの獲得が高率であったのは部分融像21例(78%)と狭い融像野11例(79%)であった。潜伏融像は治癒度Ⅰの獲得が低率であった。治癒度Ⅰを獲得できた狭い融像野では、プリズム療法が高率であった。全ての融像野で衝動性眼球運動訓練の実施率が高く、狭い融像野と部分融像においては衝動性眼球運動訓練とfusion lock trainingの組み合わせが多かった。【結論】家庭訓練は、融像野が存在する場合にはプリズム装用下で衝動性眼球運動訓練とfusion lock trainingを組み合わせ、潜伏融像では衝動性眼球運動訓練が有用であった。
- 著者
- 島田 健司 佐藤 浩一 佐藤 裕一 羽星 辰哉 花岡 真実 仁木 圴 松崎 和仁 三宅 一 高木 康志
- 出版者
- 特定非営利活動法人 日本脳神経外科救急学会 Neurosurgical Emergency
- 雑誌
- NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY (ISSN:13426214)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.2, pp.157-164, 2019 (Released:2019-10-12)
- 参考文献数
- 16
ステントリトリーバーあるいは吸引カテーテルを用いた機械的血栓回収療法は中大脳動脈遠位部(M2)を除く,前方循環系脳主幹動脈閉塞による急性期脳梗塞に対する標準的治療といえる.さらに,ステントリトリーバーと吸引カテーテルを同時に使用する併用治療に関する報告例がいくつか散見されるようになった.しかし併用療法とこれまでの単独療法を比較した文献も少なく,併用療法はまだ標準的治療とは言い難い.今回我々は当施設での前方循環系脳主幹動脈閉塞(M2を含む)による急性期脳梗塞に対し,従来のステントリトリーバー,あるいは吸引カテーテルによる単独療法と,両者を同時に使用する併用療法の治療成績を閉塞血管別に比較し,検討した.2014年8月から2018年12月に前方循環の脳主幹動脈閉塞による急性期脳梗塞に対し血栓回収療法を施行した51例を対象とした.2017年8月までは単独療法で治療し(N=31),2017年9月以降併用療法で治療した(N=20).2群間での治療転帰や再開通率,再開通までの時間を比較したが,有意差はみられなかった.そこで閉塞部位別にM2閉塞とそれ以外の閉塞血管で比較したところ,やはり治療転帰や再開通率において2群間で有意差はみられなかった.しかし手技時間がM2閉塞では併用療法において有意に長く,それ以外の閉塞血管では併用療法が短い傾向であった.併用療法は閉塞血管によっては単独療法より有用な可能性のある治療法である.
1 0 0 0 OA 利潤率の均等化と交差調整
- 著者
- 森岡 真史
- 出版者
- 経済理論学会
- 雑誌
- 季刊経済理論 (ISSN:18825184)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.3, pp.54-65, 2004-10-20 (Released:2017-04-25)
This paper critically investigates the classical preposition that the natural prices are the center of gravitation towards which market prices should move through the equalization process of industries' rates of profit. While intensively studied in 1980s and early 90s, in recent years concern for this subject seems to have declined mainly because a series of studies showed that it was by no means easy to construct a model in which rates of profit tended to be equalized. The purpose to take up this problem here is to reconsider the logic of classical argument on gravitation and to analyze systematically the dynamic nature of cross adjustment process where differentials in profit rates trigger the change of production and excess demand in each industry leads to the change of market price. In spite of the erroneous reasoning about the relation between price deviations and profit deviations, if the positive profit deviation in one industry always leads fall of its market price, the classical argument on gravitation is basically valid. The real flaw in the classical argument is that it overlooks the derived change of demand and thus fails to connect price-production movements with the balance between production and demand. This flaw can be removed by combining the adjustment of production caused by differentials in profit rates with the price movement reacting to excess demand. Thus whether the classical argument is right or wrong eventually depends on the dynamic nature of cross adjustment process. Except for few particular cases, cross adjustment brings about at best the permanent fluctuation of production and prices within a closed orbit and quite often leads to their unstable movement. The analysis in this paper demonstrates the above by multi-sector models with various assumptions on time and production period. Models consisting of three or more sectors are more likely to be instable than two-sector models. Furthermore, cross adjustment always causes instabity in discrete time models. Particularly notable is the fact that introduction of the budget constraint does not contribute to the stability of cross adjustment. It is possible to give classical cross adjustment asymptotic stability by introducing 'neo-classical' price substitution effect or 'Keynesian' quantity adjustment. However, considering the deep differences among classical, neo-classical and Keynesian economics in their theories of production adjustment, their mechanical conjugation is of little theoretical significance, even though cross adjustment extended by such conjugation may gain stability. It would be hasty to interpret the above results as 'refutation' of the classical preposition on equalization of profit rates. There are many prepositions or hypothesis in economics lacking logical 'proof' but frequently used for their usefulness or as stylized empirical fact. For the time being, the classical preposition may be regarded one of those prepositions. The model analysis in this paper throws serious doubts not to the classical preposition itself but rather to its underlying mechanisms of price-production adjustment supposed by classical economists. Especially, the mechanisms that firms increase (decrease) their production when their profit rates are above (below) the average level does not sufficiently refrect one of the most important features of capitalist economy that capitalist firms are usually under demand constraint. At any rate, future search of theoretical foundation of profit equalization should start from the different vision on the fluctuation process triggered by differentials in profit rates.
- 著者
- 岡 真理 宮下 遼 新城 郁夫 山本 薫 藤井 光 石川 清子 岡崎 弘樹 藤元 優子 福田 義昭 久野 量一 鵜戸 聡 田浪 亜央江 細田 和江 鵜飼 哲 細見 和之 阿部 賢一 呉 世宗 鈴木 克己
- 出版者
- 京都大学
- 雑誌
- 基盤研究(A)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2020-04-01
難民や移民など人間の生の経験が地球規模で国境横断的に生起する今日、人間は「祖国」なるものと様々に、痛みに満ちた関係を切り結んでいる。ネイションを所与と見なし、その同一性に収まらぬ者たちを排除する「対テロ戦争パラダイム」が世界を席巻するなか、本研究は、中東を中心に世界の諸地域を専門とする人文学研究者が協働し、文学をはじめとする文化表象における多様な「祖国」表象を通して、人文学的視点から、現代世界において人間が「祖国」をいかなるものとして生き、ネイションや地域を超えて、人間の経験をグローバルに貫く普遍的な課題とは何かを明らかにし、新たな解放の思想を創出するための基盤づくりを目指す。
1 0 0 0 OA 多様化する消費文化の問題構成 : 「第5回 消費とくらしに関する調査」の結果をもとに
- 著者
- 間々田 孝夫 廣瀬 毅士 藤岡 真之 朝倉 真粧美 中溝 一仁 野尻 洋平 ママダ タカオ ヒロセ ツヨシ フジオカ マサユキ アサクラ マサミ ナカミゾ カズヒト ノジリ ヨウヘイ Takao Mamada Tsuyoshi Hirose Masayuki Fujioka Masami Asakura Kazuhito Nakamizo Yohei Nojiri
- 雑誌
- 応用社会学研究 = The journal of applied sociology
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, pp.47-66, 2022-03-24
1 0 0 0 OA 地方自治体による「教師養成塾」事業の現状と問題点
- 著者
- 瀧本 知加 吉岡 真佐樹
- 出版者
- 日本教師教育学会
- 雑誌
- 日本教師教育学会年報 (ISSN:13437186)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.48-60, 2009-10-03 (Released:2020-12-15)
- 参考文献数
- 24
1 0 0 0 多点計測データに対する深層学習を用いた2次元動弾性逆散乱解析
- 著者
- 斎藤 隆泰 笹岡 真次 木本 和志 廣瀬 壮一
- 雑誌
- 第25回応用力学シンポジウム
- 巻号頁・発行日
- 2022-04-15